Transcriptional elongation checkpoint control in development and disease
- PMID: 23699407
- PMCID: PMC3672643
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.215137.113
Transcriptional elongation checkpoint control in development and disease
Abstract
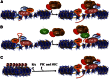
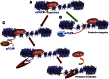
Transcriptional elongation control by RNA polymerase II and its associated factors has taken center stage as a process essential for the regulation of gene expression throughout development. In this review, we analyze recent findings on the identification of factors functioning in the regulation of the transcriptional elongation checkpoint control (TECC) stage of gene expression and how the factors' misregulation is associated with disease pathogenesis, including cancer.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; cancer; chromatin; elongation; transcription.
Figures

References
-
- Aso T, Lane WS, Conaway JW, Conaway RC 1995. Elongin (SIII): A multisubunit regulator of elongation by RNA polymerase II. Science 269: 1439–1443 - PubMed
-
- Bartholomeeusen K, Xiang Y, Fujinaga K, Peterlin BM 2012. Bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) bromodomain inhibition activate transcription via transient release of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Biol Chem 287: 36609–36616 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
