Control of translation and miRNA-dependent repression by a novel poly(A) binding protein, hnRNP-Q
- PMID: 23700384
- PMCID: PMC3660254
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001564
Control of translation and miRNA-dependent repression by a novel poly(A) binding protein, hnRNP-Q
Abstract
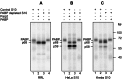
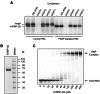
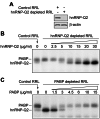
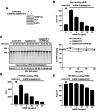
Translation control often operates via remodeling of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles. The poly(A) binding protein (PABP) simultaneously interacts with the 3' poly(A) tail of the mRNA and the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) to stimulate translation. PABP also promotes miRNA-dependent deadenylation and translational repression of target mRNAs. We demonstrate that isoform 2 of the mouse heterogeneous nuclear protein Q (hnRNP-Q2/SYNCRIP) binds poly(A) by default when PABP binding is inhibited. In addition, hnRNP-Q2 competes with PABP for binding to poly(A) in vitro. Depleting hnRNP-Q2 from translation extracts stimulates cap-dependent and IRES-mediated translation that is dependent on the PABP/poly(A) complex. Adding recombinant hnRNP-Q2 to the extracts inhibited translation in a poly(A) tail-dependent manner. The displacement of PABP from the poly(A) tail by hnRNP-Q2 impaired the association of eIF4E with the 5' m(7)G cap structure of mRNA, resulting in the inhibition of 48S and 80S ribosome initiation complex formation. In mouse fibroblasts, silencing of hnRNP-Q2 stimulated translation. In addition, hnRNP-Q2 impeded let-7a miRNA-mediated deadenylation and repression of target mRNAs, which require PABP. Thus, by competing with PABP, hnRNP-Q2 plays important roles in the regulation of global translation and miRNA-mediated repression of specific mRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GW182 proteins cause PABP dissociation from silenced miRNA targets in the absence of deadenylation.EMBO J. 2013 Apr 3;32(7):1052-65. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.44. Epub 2013 Mar 5. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23463101 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian miRNA RISC recruits CAF1 and PABP to affect PABP-dependent deadenylation.Mol Cell. 2009 Sep 24;35(6):868-80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19716330 Free PMC article.
-
[Translational control by the poly(A) binding protein: a check for mRNA integrity].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Jul-Aug;40(4):684-93. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 16913227 Review. Russian.
-
Mammalian poly(A)-binding protein is a eukaryotic translation initiation factor, which acts via multiple mechanisms.Genes Dev. 2005 Jan 1;19(1):104-13. doi: 10.1101/gad.1262905. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15630022 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of poly(A)-binding protein through PABP-interacting proteins.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:537-43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.061. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381337 Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of hnRNP Family in the Brain and Brain-Related Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jun;61(6):3578-3595. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03747-4. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 37999871 Review.
-
Determinants and implications of mRNA poly(A) tail size--does this protein make my tail look big?Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014 Oct;34:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.018. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24910447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hnRNP family: insights into their role in health and disease.Hum Genet. 2016 Aug;135(8):851-67. doi: 10.1007/s00439-016-1683-5. Epub 2016 May 23. Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27215579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The bent conformation of poly(A)-binding protein induced by RNA-binding is required for its translational activation function.RNA Biol. 2017 Mar 4;14(3):370-377. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1280224. Epub 2017 Jan 17. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28095120 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of RNA-binding proteins that partner with Lin28a to regulate Dnmt3a expression.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 27;11(1):2345. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81429-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33504840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N (2009) RNA granules: post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 430–436. - PubMed
-
- Castello A, Fischer B, Eichelbaum K, Horos R, Beckmann BM, et al. (2012) Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell 149: 1393–1406. - PubMed
-
- Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N (1999) eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 68: 913–963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

