Anatomy and function of cholinergic C bouton inputs to motor neurons
- PMID: 23701140
- PMCID: PMC3867887
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12063
Anatomy and function of cholinergic C bouton inputs to motor neurons
Erratum in
- J Anat. 2014 Apr;224(4):528
-
Corrigendum.J Anat. 2014 Apr;224(4):528. doi: 10.1111/joa.12158. Epub 2014 Jan 2. J Anat. 2014. PMID: 28349524 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Motor control circuitry of the central nervous system must be flexible so that motor behaviours can be adapted to suit the varying demands of different states, developmental stages, and environments. Flexibility in motor control is largely provided by neuromodulatory systems which can adjust the output of motor circuits by modulating the properties and connectivity of neurons within them. The spinal circuitry which controls locomotion is subject to a range of neuromodulatory influences, including some which are intrinsic to the spinal cord. One such intrinsic neuromodulatory system, for which a wealth of anatomical information has recently been combined with new physiological data, is the C bouton system. C boutons are large, cholinergic inputs to motor neurons which were first described over 40 years ago but whose source and function have until recently remained a mystery. In this review we discuss how the convergence of anatomical, molecular genetic and physiological data has recently led to significant advances in our understanding of this unique neuromodulatory system. We also highlight evidence that C boutons are involved in spinal cord injury and disease, revealing their potential as targets for novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: C terminal; motor control; neuromodulation; spinal cord.
© 2013 Anatomical Society.
Figures



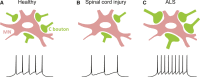
Similar articles
-
Spinal cholinergic interneurons regulate the excitability of motoneurons during locomotion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2448-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611134104. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17287343 Free PMC article.
-
A cluster of cholinergic premotor interneurons modulates mouse locomotor activity.Neuron. 2009 Dec 10;64(5):645-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.10.017. Neuron. 2009. PMID: 20005822 Free PMC article.
-
Pitx2 cholinergic interneurons are the source of C bouton synapses on brainstem motor neurons.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 20;9(1):4936. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39996-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30894556 Free PMC article.
-
Swimming against the tide: investigations of the C-bouton synapse.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Sep 18;8:106. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00106. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 25278842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity-dependent synaptic plasticity and metaplasticity in spinal motor networks.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(24):4498-508. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319240014. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23360279 Review.
Cited by
-
Fast Blue and Cholera Toxin-B Survival Guide for Alpha-Motoneurons Labeling: Less Is Better in Young B6SJL Mice, but More Is Better in Aged C57Bl/J Mice.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 20;10(2):141. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020141. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829635 Free PMC article.
-
Transynaptic Action of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A at Central Cholinergic Boutons.J Neurosci. 2018 Nov 28;38(48):10329-10337. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0294-18.2018. Epub 2018 Oct 12. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30315128 Free PMC article.
-
Acetylcholine and spinal locomotor networks: The insider.Physiol Rep. 2021 Feb;9(3):e14736. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14736. Physiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33527727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPM8-mediated cutaneous stimulation modulates motor neuron activity during treadmill stepping in mice.J Physiol Sci. 2019 Nov;69(6):931-938. doi: 10.1007/s12576-019-00707-3. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Physiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31482469 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord from body donors is suitable for multicolor immunofluorescence.Histochem Cell Biol. 2023 Jan;159(1):23-45. doi: 10.1007/s00418-022-02154-5. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Histochem Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36201037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Saif A, Bohlega S, Al-Mohanna F. Loss of ERLIN2 function leads to juvenile primary lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:510–516. - PubMed
-
- Arvidsson U, Svedlund J, Lagerback PA, et al. An ultrastructural study of the synaptology of gamma-motoneurones during the postnatal development in the cat. Brain Res. 1987;465:303–312. - PubMed
-
- Arvidsson U, Riedl M, Elde R, et al. Vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) protein: a novel and unique marker for cholinergic neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. J Comp Neurol. 1997;378:454–467. - PubMed
-
- Barber RP, Phelps PE, Houser CR, et al. The morphology and distribution of neurons containing choline acetyltransferase in the adult rat spinal cord: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1984;229:329–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

