Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin injection in healthy Chinese volunteers and dosing regimen optimization
- PMID: 23701411
- PMCID: PMC4285945
- DOI: 10.1111/jcpt.12074
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levofloxacin injection in healthy Chinese volunteers and dosing regimen optimization
Abstract
What is known and objective: The pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) of levofloxacin were investigated following administration of levofloxacin injection in healthy Chinese volunteers for optimizing dosing regimen.
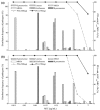
Methods: The PK study included single-dose (750 mg/150 mL) and multiple-dose (750 mg/150 mL once daily for 7 days) phases. The concentration of levofloxacin in blood and urine was determined using HPLC method. Both non-compartmental and compartmental analyses were performed to estimate PK parameters. Taking fC(max) /MIC ≥5 and fAUC(24 h) /MIC ≥30 as a target, the cumulative fraction of response (CFR) of levofloxacin 750 mg for treatment of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) was calculated using Monte Carlo simulation. The probability of target attainment (PTA) of levofloxacin at various minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) was also evaluated.
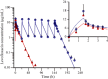
Results and discussion: The results of PK study showed that the C(max) and AUC(0-∞) of levofloxacin were 14·94 μg/mL and 80·14 μg h/mL following single-dose infusion of levofloxacin. The half-life and average cumulative urine excretion ratio within 72 h post-dosing were 7·75 h and 86·95%, respectively. The mean C(ss,max), C(ss,min) and AUC(0-τ) of levofloxacin at steady state following multiple doses were 13·31 μg/mL, 0·031 μg/mL and 103·7 μg h/mL, respectively. The accumulation coefficient was 1·22. PK/PD analysis revealed that the CFR value of levofloxacin 750-mg regimen against Streptococcus pneumoniae was 96·2% and 95·4%, respectively, in terms of fC(max) /MIC and fAUC/MIC targets.
What is new and conclusion: The regimen of 750-mg levofloxacin once daily provides a satisfactory PK/PD profile against the main pathogenic bacteria of CAP, which implies promising clinical and bacteriological efficacy for patients with CAP. A large-scale clinical study is warranted to confirm these results.
Keywords: Monte Carlo simulation; healthy volunteer; levofloxacin; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Wang F, Zhang Y, editors. Practical antimicrobial therapeutics. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House; 2004.
-
- Friedman H, Song X, Crespi S, Navaratnam P. Comparative analysis of length of stay, total costs, and treatment success between intravenous moxifloxacin 400 mg and levofloxacin 750 mg among hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Value Health. 2009;12:1135–1143. - PubMed
-
- Frei CR, Jaso TC, Mortensen EM, et al. Medical resource utilization among community-acquired pneumonia patients initially treated with levofloxacin 750 mg daily versus ceftriaxone 1000 mg plus azithromycin 500 mg daily: a US-based study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009;25:859–868. - PubMed
-
- Schein J, Janagap-Benson C, Grant R, Sikirica V, Doshi D, Olson W. A comparison of levofloxacin and moxifloxacin use in hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) patients in the US: focus on length of stay. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24:895–906. - PubMed
-
- Lynch JP, 3rd, File TM, Jr, Zhanel GG. Levofloxacin for the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2006;4:725–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

