RNA protein interaction in neurons
- PMID: 23701460
- PMCID: PMC3889695
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062912-114322
RNA protein interaction in neurons
Abstract
Neurons have their own systems for regulating RNA. Several multigene families encode RNA binding proteins (RNABPs) that are uniquely expressed in neurons, including the well-known neuron-specific markers ELAV and NeuN and the disease antigen NOVA. New technologies have emerged in recent years to assess the function of these proteins in vivo, and the answers are yielding insights into how and why neurons may regulate RNA in special ways-to increase cellular complexity, to localize messenger RNA (mRNA) spatially, and to regulate their expression in response to synaptic stimuli. The functions of such restricted neuronal proteins are likely to be complemented by more widely expressed RNABPs that may themselves have developed specialized functions in neurons, including Argonaute/microRNAs (miRNAs). Here we review what is known about such RNABPs and explore the potential biologic and neurologic significance of neuronal RNA regulatory systems.
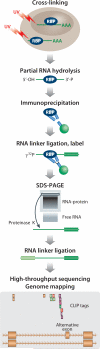
Figures
References
-
- Aakalu G, Smith WB, Nguyen N, Jiang C, Schuman EM. Dynamic visualization of local protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Neuron. 2001;30:489–502. - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu W, Okano HJ, Osumi N, Inoue T, Nakamura S, Sakakibara SI, Miura M, Matsuo N, Darnell RB, Okano H. Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:9885–9890. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amara SG, Jonas V, Rosenfeld MG, Ong ES, Evans R. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982;298:240–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

