The impact of a school-based water supply and treatment, hygiene, and sanitation programme on pupil diarrhoea: a cluster-randomized trial
- PMID: 23702047
- PMCID: PMC9151148
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268813001118
The impact of a school-based water supply and treatment, hygiene, and sanitation programme on pupil diarrhoea: a cluster-randomized trial
Abstract
The impact of improved water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) access on mitigating illness is well documented, although impact of school-based WASH on school-aged children has not been rigorously explored. We conducted a cluster-randomized trial in Nyanza Province, Kenya to assess the impact of a school-based WASH intervention on diarrhoeal disease in primary-school pupils. Two study populations were used: schools with a nearby dry season water source and those without. Pupils attending 'water-available' schools that received hygiene promotion and water treatment (HP&WT) and sanitation improvements showed no difference in period prevalence or duration of illness compared to pupils attending control schools. Those pupils in schools that received only the HP&WT showed similar results. Pupils in 'water-scarce' schools that received a water-supply improvement, HP&WT and sanitation showed a reduction in diarrhoea incidence and days of illness. Our study revealed mixed results on the impact of improvements to school WASH improvements on pupil diarrhoea.
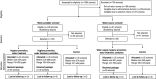
Figures
References
-
- Liu L, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet 2012; 379: 2151–2161. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2013; 380: 2197–2223. - PubMed
-
- Fischer Walker CL, Black RE. Diarrhoea morbidity and mortality in older children, adolescents, and adults. Epidemiology and Infection 2010; 138: 1215–1226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

