Diabetes and altered glucose metabolism with aging
- PMID: 23702405
- PMCID: PMC3664017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2013.02.010
Diabetes and altered glucose metabolism with aging
Abstract
Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance affect a substantial proportion of older adults. Abnormal glucose metabolism is not a necessary component of aging. Older adults with diabetes and altered glucose status likely represent a subset of the population at high risk for complications and adverse geriatric syndromes. Goals for treatment of diabetes in the elderly include control of hyperglycemia, prevention and treatment of diabetic complications, avoidance of hypoglycemia, and preservation of quality of life. Research exploring associations of dysglycemia and insulin resistance with the development of adverse outcomes in the elderly may ultimately inform use of future glucose-lowering therapies in this population.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures:
Conflict of interest (RK, JE): None
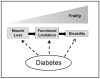
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early metabolic markers of the development of dysglycemia and type 2 diabetes and their physiological significance.Diabetes. 2013 May;62(5):1730-7. doi: 10.2337/db12-0707. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23160532 Free PMC article.
-
Improving glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: Stimulate insulin secretion or provide beta-cell rest?Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Sep;19(9):1205-1213. doi: 10.1111/dom.12935. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 28295962 Review.
-
NMDAR antagonists for the treatment of diabetes mellitus-Current status and future directions.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Sep;19 Suppl 1:95-106. doi: 10.1111/dom.13017. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 28880473 Review.
-
[Insulin secretion and insulin resistance].Nihon Rinsho. 2013 Nov;71(11):1936-40. Nihon Rinsho. 2013. PMID: 24397162 Review. Japanese.
-
Pulsatile insulin secretion, impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes.Mol Aspects Med. 2015 Apr;42:61-77. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Mol Aspects Med. 2015. PMID: 25637831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Age impacts ability of aspartate-alanine aminotransferase ratio to predict advanced fibrosis in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Jun;60(6):1825-31. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3529-8. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25708897
-
[Glucose metabolism in older patients].Internist (Berl). 2019 Feb;60(2):133-140. doi: 10.1007/s00108-018-0542-y. Internist (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30617701 Review. German.
-
Evaluation of Tibial Hemodynamic Response to Glucose Tolerance Test in Young Healthy Males and Females.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 20;15(18):4062. doi: 10.3390/nu15184062. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764845 Free PMC article.
-
Weight Loss and Exercise Differentially Affect Insulin Sensitivity, Body Composition, Cardiorespiratory Fitness, and Muscle Strength in Older Adults With Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022 May 5;77(5):1088-1097. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glab240. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34406407 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Aging Effects on Absolute and Relative Estrogen Receptor Variant Gene Expression Levels in Male Versus Female Rat Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone Neurons.J Integr Neurosci. 2025 Jun 23;24(6):38142. doi: 10.31083/JIN38142. J Integr Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40613376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Public Health and Aging: Trends in Aging --- United States and Worldwide. JAMA. 2003;289:1371–3. - PubMed
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, et al. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Decker FH, Luo H, et al. Trends in the prevalence and comorbidities of diabetes mellitus in nursing home residents in the United States: 1995-2004. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010;58:724–30. - PubMed
-
- Shimokata H, Muller DC, Fleg JL, et al. Age as an independent determinant of glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 1991;40:44–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

