Resting-state fMRI in the Human Connectome Project
- PMID: 23702415
- PMCID: PMC3720828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.039
Resting-state fMRI in the Human Connectome Project
Abstract
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rfMRI) allows one to study functional connectivity in the brain by acquiring fMRI data while subjects lie inactive in the MRI scanner, and taking advantage of the fact that functionally related brain regions spontaneously co-activate. rfMRI is one of the two primary data modalities being acquired for the Human Connectome Project (the other being diffusion MRI). A key objective is to generate a detailed in vivo mapping of functional connectivity in a large cohort of healthy adults (over 1000 subjects), and to make these datasets freely available for use by the neuroimaging community. In each subject we acquire a total of 1h of whole-brain rfMRI data at 3 T, with a spatial resolution of 2×2×2 mm and a temporal resolution of 0.7s, capitalizing on recent developments in slice-accelerated echo-planar imaging. We will also scan a subset of the cohort at higher field strength and resolution. In this paper we outline the work behind, and rationale for, decisions taken regarding the rfMRI data acquisition protocol and pre-processing pipelines, and present some initial results showing data quality and example functional connectivity analyses.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


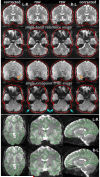

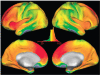

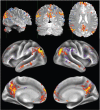


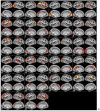


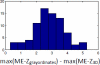
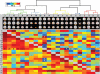
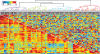


Similar articles
-
The Lifespan Human Connectome Project in Aging: An overview.Neuroimage. 2019 Jan 15;185:335-348. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30332613 Free PMC article.
-
Pushing spatial and temporal resolution for functional and diffusion MRI in the Human Connectome Project.Neuroimage. 2013 Oct 15;80:80-104. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.012. Epub 2013 May 21. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23702417 Free PMC article.
-
Human Connectome Project-style resting-state functional MRI at 7 Tesla using radiofrequency parallel transmission.Neuroimage. 2019 Jan 1;184:396-408. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.09.038. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30237033 Free PMC article.
-
Learning and comparing functional connectomes across subjects.Neuroimage. 2013 Oct 15;80:405-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.007. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23583357 Review.
-
The parcellation-based connectome: limitations and extensions.Neuroimage. 2013 Oct 15;80:397-404. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.053. Epub 2013 Apr 1. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23558097 Review.
Cited by
-
Strength-dependent perturbation of whole-brain model working in different regimes reveals the role of fluctuations in brain dynamics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Nov 2;18(11):e1010662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010662. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36322525 Free PMC article.
-
Individual-specific features of brain systems identified with resting state functional correlations.Neuroimage. 2017 Feb 1;146:918-939. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.08.032. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Neuroimage. 2017. PMID: 27640749 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Issues in Glioma Using Imaging Data: The Challenge of Numerical Twinning.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 15;12(24):7706. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247706. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Default-mode network streams for coupling to language and control systems.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 21;117(29):17308-17319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005238117. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32632019 Free PMC article.
-
Network Representation of fMRI Data Using Visibility Graphs: The Impact of Motion and Test-Retest Reliability.Neuroinformatics. 2024 Apr;22(2):107-118. doi: 10.1007/s12021-024-09652-y. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Neuroinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38332409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckmann C, Smith S. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. on Medical Imaging. 2004;23(2):137–152. [Beckmann and Smith, 2004] - PubMed
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin F, V. M. H, Hyde J. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1995;34:537–541. [Biswal et al., 1995] - PubMed
-
- Boxerman JL, Bandettini PA, Kwong KK, Baker JR, Davis TL, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM. The intravascular contribution to FMRI signal change: Monte Carlo modeling and diffusion-weighted studies in vivo. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1995;34(1):4–10. [Boxerman et al., 1995] - PubMed
-
- Breuer FA, Blaimer M, Heidemann RM, Mueller MF, Griswold MA, Jakob PM. Controlled aliasing in parallel imaging results in higher acceleration (CAIPIRINHA) for multi-slice imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53(3):684–91. [Breuer et al., 2005] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 1U54MH091657-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 098369/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- F30-MH097312/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH100872/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS076408/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K006673/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P41-RR08079/EB015894/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB015894/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- F30 MH097312/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR008079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30-NS057091/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MH091657/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057091/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

