Immunology of age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 23702979
- PMCID: PMC3941009
- DOI: 10.1038/nri3459
Immunology of age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of blindness in aged individuals. Recent advances have highlighted the essential role of immune processes in the development, progression and treatment of AMD. In this Review we discuss recent discoveries related to the immunological aspects of AMD pathogenesis. We outline the diverse immune cell types, inflammatory activators and pathways that are involved. Finally, we discuss the future of inflammation-directed therapeutics to treat AMD in the growing aged population.
Figures
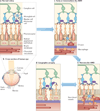
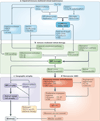
Comment in
-
A role for IL-17 in age-related macular degeneration.Nat Rev Immunol. 2013 Sep;13(9):701. doi: 10.1038/nri3459-c1. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23969738 No abstract available.
References
-
- The Global Economic Cost of Visual Impairment. AMD Alliance International. 2010 [online], http://www.icoph.org/resources/146/The-Global-Economic-Cost-of-Visual-Im....
-
- Haines JL, et al. Complement factor H variant increases the risk of age-related macular degeneration. Science. 2005;308:419–421. - PubMed
-
- Edwards AO, et al. Complement factor H polymorphism and age-related macular degeneration. Science. 2005;308:421–424. - PubMed
-
-
Klein RJ, et al. Complement factor H polymorphism in age-related macular degeneration. Science. 2005;308:385–389. References – are landmark studies showing increased statistical risk of AMD in individuals who have a single CFH polymorphism these studies were the first of their kind for a complex human disease.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000117/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY018836/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- GM099111/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM099111/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY020672/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- AI041592/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL112303/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR0483335/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY018836/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY020672/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- HL112303/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AR007279/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01EY022238/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007279/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000117/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041592/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022238/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

