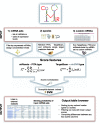
ComiR: Combinatorial microRNA target prediction tool
- PMID: 23703208
- PMCID: PMC3692082
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt379
ComiR: Combinatorial microRNA target prediction tool
Abstract
ComiR is a web tool for combinatorial microRNA (miRNA) target prediction. Given an messenger RNA (mRNA) in human, mouse, fly or worm genomes, ComiR computes the potential of being targeted by a set of miRNAs, each of which can have zero, one or more targets on its 3'untranslated region. In determining the regulatory potential of an mRNA from a set of miRNAs, ComiR uses user-provided miRNA expression levels in a combination of appropriate thermodynamic modeling and machine learning techniques to make more accurate predictions. For each gene, ComiR returns the probability of being a functional target of a set of miRNAs, which depends on the relative miRNA expression levels. The tool provides a user-friendly interface to input a miRNA expression table containing many sample information and filter out the most relevant miRNAs. ComiR results can be downloaded or visualized on a table, which can then be used to select the most relevant targets and to compare the results obtained with different miRNA expression input. ComiR is freely available for academic use at http://www.benoslab.pitt.edu/comir/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An improvement of ComiR algorithm for microRNA target prediction by exploiting coding region sequences of mRNAs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Sep 16;21(Suppl 8):201. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3519-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32938407 Free PMC article.
-
Novel modeling of combinatorial miRNA targeting identifies SNP with potential role in bone density.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(12):e1002830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002830. Epub 2012 Dec 20. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 23284279 Free PMC article.
-
DIANA-mirExTra v2.0: Uncovering microRNAs and transcription factors with crucial roles in NGS expression data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jul 8;44(W1):W128-34. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw455. Epub 2016 May 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27207881 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of human microRNA targets.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;342:101-13. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-123-1:101. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16957370 Review.
-
Desperately seeking microRNA targets.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010 Oct;17(10):1169-74. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1921. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20924405 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth of glioblastoma is inhibited by miR-133-mediated EGFR suppression.Tumour Biol. 2015 Dec;36(12):9553-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3724-4. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26138587
-
Roles of microRNAs in psoriasis: Immunological functions and potential biomarkers.Exp Dermatol. 2017 Apr;26(4):359-367. doi: 10.1111/exd.13249. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Exp Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27783430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common features of microRNA target prediction tools.Front Genet. 2014 Feb 18;5:23. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00023. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24600468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldosterone regulates microRNAs in the cortical collecting duct to alter sodium transport.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Nov;25(11):2445-57. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013090931. Epub 2014 Apr 17. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24744440 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of miR-638 in vitro promotes cell invasion and a mesenchymal-like transition by influencing SOX2 expression in colorectal carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer. 2014 May 23;13:118. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-118. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24885288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Kertesz M, Iovino N, Unnerstall U, Gaul U, Segal E. The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:1278–1284. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources