Rapid rise in hypertension and nephropathy in youth with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial
- PMID: 23704672
- PMCID: PMC3661847
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2420
Rapid rise in hypertension and nephropathy in youth with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial
Erratum in
- Diabetes Care. 2013 Aug;36(8):2448
Abstract
Objective: Among adolescents with type 2 diabetes, there is limited information regarding incidence and progression of hypertension and microalbuminuria. Hypertension and microalbuminuria assessments made during the TODAY clinical trial were analyzed for effect of treatment, glycemic control, sex, and race/ethnicity.
Research design and methods: A cohort of 699 adolescents, 10-17 years of age, <2 years duration of type 2 diabetes, BMI ≥ 85%, HbA1c ≤ 8% on metformin therapy, controlled blood pressure (BP), and calculated creatinine clearance >70 mL/min, were randomized to metformin, metformin plus rosiglitazone, or metformin plus intensive lifestyle intervention. Primary study outcome was loss of glycemic control for 6 months or sustained metabolic decompensation requiring insulin. Hypertension and microalbuminuria were managed aggressively with standardized therapy to maintain BP <130/80 or <95th percentile for age, sex, and height and microalbuminuria <30 μg/mg.
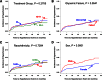
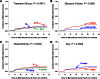
Results: In this cohort, 319 (45.6%) reached primary study outcome, and 11.6% were hypertensive at baseline and 33.8% by end of study (average follow-up 3.9 years). Male sex and higher BMI significantly increased the risk for hypertension. Microalbuminuria was found in 6.3% at baseline and rose to 16.6% by end of study. Diagnosis of microalbuminuria was not significantly different between treatment arms, sex, or race/ethnicity, but higher levels of HbA1c were significantly related to risk of developing microalbuminuria.
Conclusions: Prevalence of hypertension and microalbuminuria increased over time among adolescents with type 2 diabetes regardless of diabetes treatment. The greatest risk for hypertension was male sex and higher BMI. The risk for microalbuminuria was more closely related to glycemic control.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00081328.
Figures
Comment in
-
“TODAY” reflects on the changing “faces” of type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2013 Jun;36(6):1732-4. doi: 10.2337/dc13-0765. Diabetes Care. 2013. PMID: 23844434 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Retnakaran R, Cull CA, Thorne KI, Adler AI, Holman RR, UKPDS Study Group Risk factors for renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study 74. Diabetes 2006;55:1832–1839 - PubMed
-
- Bilous R. Microvascular disease: what does the UKPDS tell us about diabetic nephropathy? Diabet Med 2008;25(Suppl. 2):25–29 - PubMed
-
- Writing Team for the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Research Group Sustained effect of intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus on development and progression of diabetic nephropathy: the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. JAMA 2003;290:2159–2167 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR014467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-14467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00043-45/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 01-RR-00084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000130/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

