Lipid and inflammatory cardiovascular risk worsens over 3 years in youth with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial
- PMID: 23704675
- PMCID: PMC3661790
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2388
Lipid and inflammatory cardiovascular risk worsens over 3 years in youth with type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: Type 2 diabetes increases cardiovascular risk. We examined lipid profiles and inflammatory markers in 699 youth with recent-onset type 2 diabetes in the TODAY clinical trial and compared changes across treatment groups: metformin alone (M), metformin plus rosiglitazone (M+R), and metformin plus intensive lifestyle program (M+L).
Research design and methods: Multiethnic youth with type 2 diabetes received M, M+R, or M+L. Statin drugs were begun for LDL cholesterol (LDL) ≥ 130 mg/dL or triglycerides ≥ 300 mg/dL. Lipids, apolipoprotein B (apoB), LDL particle size, high-sensitivity c-reactive protein (hsCRP), homocysteine, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and HbA1c were measured over 36 months or until loss of glycemic control.
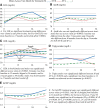
Results: LDL, apoB, triglycerides, and non-HDL cholesterol (HDL) rose over 12 months and then stabilized over the next 24 months. Participants with LDL ≥ 130 mg/dL or using LDL-lowering therapy increased from 4.5 to 10.7% over 36 months, while 55.9% remained at LDL goal (<100 mg/dL) over that time. Treatment group did not impact LDL, apoB, or non-HDL. Small dense LDL (particle size, ≤ 0.263 relative flotation rate) was most common in M. Triglycerides were lower in M+L than M, and M+L attenuated the negative effect of hyperglycemia on triglycerides and HDL in females. hsCRP, PAI-1, and homocysteine increased over time. However, hsCRP was lower in M+R compared with M or M+L.
Conclusions: Dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation were common in youth with type 2 diabetes and worsened over time. Diabetes treatment, despite some treatment group differences in lipid and inflammatory marker change over time, is generally inadequate to control this worsening risk.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00081328.
Figures

References
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837–853 - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). Lancet 1998;352:854–865 - PubMed
-
- Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1577–1589 - PubMed
-
- McGill HC, Jr, McMahan CA, Malcom GT, Oalmann MC, Strong JP, Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) Research Group Relation of glycohemoglobin and adiposity to atherosclerosis in youth. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1995;15:431–440 - PubMed
-
- Gidding SS. Assembling evidence to justify prevention of atherosclerosis beginning in youth. Circulation 2010;122:2493–2494 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR014467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00043-45/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR01066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-61242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR14467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR00084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000130/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

