A novel sphingolipid-TORC1 pathway critically promotes postembryonic development in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 23705068
- PMCID: PMC3660743
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.00429
A novel sphingolipid-TORC1 pathway critically promotes postembryonic development in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
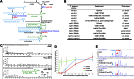
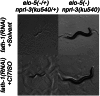
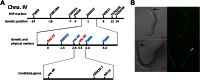
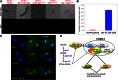
Regulation of animal development in response to nutritional cues is an intensely studied problem related to disease and aging. While extensive studies indicated roles of the Target of Rapamycin (TOR) in sensing certain nutrients for controlling growth and metabolism, the roles of fatty acids and lipids in TOR-involved nutrient/food responses are obscure. Caenorhabditis elegans halts postembryonic growth and development shortly after hatching in response to monomethyl branched-chain fatty acid (mmBCFA) deficiency. Here, we report that an mmBCFA-derived sphingolipid, d17iso-glucosylceramide, is a critical metabolite in regulating growth and development. Further analysis indicated that this lipid function is mediated by TORC1 and antagonized by the NPRL-2/3 complex in the intestine. Strikingly, the essential lipid function is bypassed by activating TORC1 or inhibiting NPRL-2/3. Our findings uncover a novel lipid-TORC1 signaling pathway that coordinates nutrient and metabolic status with growth and development, advancing our understanding of the physiological roles of mmBCFAs, ceramides, and TOR. DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.00429.001.
Keywords: C. elegans; NPRL; branched-chain fatty acid; glucosylceramide; growth arrest; nutrient sensing; target of rapamycin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Intestinal apical polarity mediates regulation of TORC1 by glucosylceramide in C. elegans.Genes Dev. 2015 Jun 15;29(12):1218-23. doi: 10.1101/gad.263483.115. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 26109047 Free PMC article.
-
A Lipid-TORC1 Pathway Promotes Neuronal Development and Foraging Behavior under Both Fed and Fasted Conditions in C. elegans.Dev Cell. 2015 May 4;33(3):260-71. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2015.02.015. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Dev Cell. 2015. PMID: 25892013
-
Twists and turns--How we stepped into and had fun in the "boring" lipid field.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Nov;58(11):1073-83. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4949-6. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26511515 Review.
-
The intestinal TORC2 signaling pathway contributes to associative learning in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2017 May 25;12(5):e0177900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177900. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542414 Free PMC article.
-
TOR Signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans Development, Metabolism, and Aging.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):329-360. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302504. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31594908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serum- and Glucocorticoid-Inducible Kinase-1 (SGK-1) Plays a Role in Membrane Trafficking in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 26;10(6):e0130778. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130778. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26115433 Free PMC article.
-
Deregulation of Mitochondrial Calcium Handling Due to Presenilin Loss Disrupts Redox Homeostasis and Promotes Neuronal Dysfunction.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Aug 24;11(9):1642. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091642. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139715 Free PMC article.
-
SEA and GATOR 10 Years Later.Cells. 2021 Oct 8;10(10):2689. doi: 10.3390/cells10102689. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TORC1 phosphoproteome in C. elegans reveals roles in transcription and autophagy.iScience. 2022 Mar 31;25(5):104186. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104186. eCollection 2022 May 20. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35479415 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Meets Metabolomics-The WormJam Consensus Model as Basis for Metabolic Studies in the Model Organism Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Nov 14;5:96. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00096. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30488036 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

