Bordetella bronchiseptica Pneumonia in an Extremely-Low-Birth-Weight Neonate
- PMID: 23705092
- PMCID: PMC3653527
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1284223
Bordetella bronchiseptica Pneumonia in an Extremely-Low-Birth-Weight Neonate
Abstract
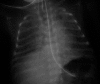
Bordetella bronchiseptica, a gram-negative coccobacillus, is a common veterinary pathogen. In both domestic and wild animals, this bacterium causes respiratory infections including infectious tracheobronchitis in dogs and atrophic rhinitis in swine. Human infections are rare and have been documented in immunocompromised hosts. Here, we describe an extremely-low-birth-weight infant with B. bronchiseptica pneumonia. This is the first report that describes the microorganism's responsibility in causing nosocomial infection in a preterm neonate. He recovered uneventfully after a course of meropenem. It is possible that the bacteria colonize the respiratory tracts of our health care workers or parents who may have had contact with pets and then transmitted the bacterium to our patient. Follow-up until 21 months of age showed normal growth and development. He did not suffer from any significant residual respiratory disease.
Keywords: Bordetella bronchiseptica; extremely low birth weight; neonate; preterm.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica: a rare cause of meningitis.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Dec 3;20(1):922. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05668-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33272197 Free PMC article.
-
A wolf in sheep's clothing: Dogs confer an unrecognized risk for their immunocompromised master.Respir Med Case Rep. 2022 May 25;38:101672. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101672. eCollection 2022. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35651518 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients.Clin Infect Dis. 1999 May;28(5):1095-9. doi: 10.1086/514761. Clin Infect Dis. 1999. PMID: 10452641
-
Bordetella bronchiseptica pneumonia: beware of the dog!BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Apr 27;2018:bcr2018224588. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224588. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29703836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Bordetella bronchiseptica-associated acute chest syndrome in a child with sickle cell disease].Arch Pediatr. 2011 Jan;18(1):41-4. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2010.09.015. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Arch Pediatr. 2011. PMID: 21036565 Review. French.
References
-
- Ner Z, Ross L A, Horn M V. et al.Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in pediatric lung transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant. 2003;7:413–417. - PubMed
-
- Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A. et al.Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet. 2003;35:32–40. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources