Syndecan-2 is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells through interactions with extracellular matrix produced by stromal fibroblasts
- PMID: 23705906
- PMCID: PMC3681618
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-25
Syndecan-2 is upregulated in colorectal cancer cells through interactions with extracellular matrix produced by stromal fibroblasts
Abstract
Background: The extracellular matrix (ECM) influences the structure, viability and functions of cells and tissues. Recent evidence indicates that tumor cells and stromal cells interact through direct cell-cell contact, the production of ECM components and the secretion of growth factors. Syndecans are a family of transmembrane heparan sulfate proteoglycans that are involved in cell adhesion, motility, proliferation and differentiation. Syndecan-2 has been found to be highly expressed in colorectal cancer cell lines and appears to be critical for cancer cell behavior. We have examined the effect of stromal fibroblast-produced ECM on the production of proteoglycans by colorectal cancer cell lines.
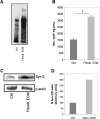
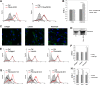
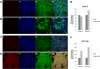
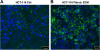
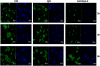
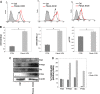
Results: Our results showed that in a highly metastatic colorectal cancer cell line, HCT-116, syndecan-2 expression is enhanced by fibroblast ECM, while the expression of other syndecans decreased. Of the various components of the stromal ECM, fibronectin was the most important in stimulating the increase in syndecan-2 expression. The co-localization of syndecan-2 and fibronectin suggests that these two molecules are involved in the adhesion of HCT-116 cells to the ECM. Additionally, we demonstrated an increase in the expression of integrins alpha-2 and beta-1, in addition to an increase in the expression of phospho-FAK in the presence of fibroblast ECM. Furthermore, blocking syndecan-2 with a specific antibody resulted in a decrease in cell adhesion, migration, and organization of actin filaments.
Conclusions: Overall, these results show that interactions between cancer cells and stromal ECM proteins induce significant changes in the behavior of cancer cells. In particular, a shift from the expression of anti-tumorigenic syndecans to the tumorigenic syndecan-2 may have implications in the migratory behavior of highly metastatic tumor cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Syndecan-2 expression in colorectal cancer-derived HT-29 M6 epithelial cells induces a migratory phenotype.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Aug 31;286(4):742-51. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.5459. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11520060
-
FAP-overexpressing fibroblasts produce an extracellular matrix that enhances invasive velocity and directionality of pancreatic cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2011 Jun 13;11:245. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-245. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21668992 Free PMC article.
-
Heparanase degrades syndecan-1 and perlecan heparan sulfate: functional implications for tumor cell invasion.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):8047-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304872200. Epub 2003 Nov 20. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14630925
-
Syndecans in heart fibrosis.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Sep;365(3):539-52. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2454-2. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 27411689 Review.
-
Syndecan family of cell surface proteoglycans: developmentally regulated receptors for extracellular effector molecules.Experientia. 1995 Sep 29;51(9-10):863-72. doi: 10.1007/BF01921737. Experientia. 1995. PMID: 7556568 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-218 affects the ECM composition and cell biomechanical properties of glioblastoma cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jul;26(14):3913-3930. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17428. Epub 2022 Jun 15. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35702951 Free PMC article.
-
The methylation of SDC2 and TFPI2 defined three methylator phenotypes of colorectal cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Feb 28;22(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02175-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35227195 Free PMC article.
-
The Glycosaminoglycan Side Chains and Modular Core Proteins of Heparan Sulphate Proteoglycans and the Varied Ways They Provide Tissue Protection by Regulating Physiological Processes and Cellular Behaviour.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 14;24(18):14101. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814101. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Syndecans in Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Cancer.J Histochem Cytochem. 2020 Dec;68(12):863-870. doi: 10.1369/0022155420930112. Epub 2020 Jul 6. J Histochem Cytochem. 2020. PMID: 32623937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syndecans as Cell Surface Receptors in Cancer Biology. A Focus on their Interaction with PDZ Domain Proteins.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Feb 2;7:10. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00010. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26869927 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams JC, Watt FM. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. Development. 1993;117:1183–1198. - PubMed
-
- Grinnell F. Wound repair, keratinocyte activation and integrin modulation. J Cell Sci. 1992;101:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Bosman FT, De Bruïne A, Flohi C, van der Wurff A, Ten Kate J, Dinjens WW. Epithelial-stromal interactions in colon cancer. Int J Dev Biol. 1993;37:203–211. - PubMed
-
- Ekblom P, Aufderheide E. Stimulation of tenascin expression in mesenchyme by epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Int J Dev Biol. 1989;33:71–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

