Costs and outcome for serious hand and arm injuries during the first year after trauma - a prospective study
- PMID: 23706070
- PMCID: PMC3681586
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-501
Costs and outcome for serious hand and arm injuries during the first year after trauma - a prospective study
Abstract
Background: To study costs and outcome for serious hand and arm injuries during the first year after the trauma.
Methods: In patients with a Hand Injury Severity Score (HISS) > 50, DASH and EQ-5D scores as well as factors related to costs within the health care sector, costs due to lost production and total costs were evaluated. Cox-regression analysis stratifying for mechanism of injury was used to analyse return to work.
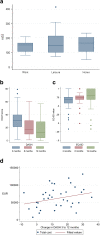
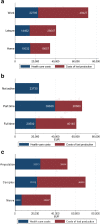
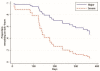
Results: The majority of the 45 included patients (median 42 years 16-64) were men with severe (n = 9) or major (n = 36) injuries with different type of injuries (amputations n = 13; complex injuries n = 18; major nerve injuries/full house n = 13; burn injury n = 1). DASH and EQ-5D decreased and increased, respectively, significantly over time during one year. Total costs (+34%) and costs of lost production were highest for persons injured at work. Factors associated with higher health care costs were age >50 years (+52%), injury at work (+40%) and partial labour market activity (+66%). Costs of lost production had a significant role in total costs of injury. Patients with major injuries had longer duration of sick leave. Patients with severe injuries were more likely to return to work [(RR 3.76 (95% CI 1.38-10.22) from Cox regression, controlling for age, gender and presence of nerve injury].
Conclusions: Despite the fact that work environments have constantly improved over the last decades, we found that hand injuries at work were most costly both in terms of health care and costs of lost production, although the severity, i.e. HISS, did not differ from injuries occurring at home or during leisure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prospective study of patients with injuries to the hand and forearm: costs, function, and general health.Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2005;39(6):360-9. doi: 10.1080/02844310500340046. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2005. PMID: 16298809
-
Disability and health after replantation or revascularisation in the upper extremity in a population in southern Sweden - a retrospective long time follow up.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014 Mar 10;15:73. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-15-73. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014. PMID: 24612503 Free PMC article.
-
[Predictive value of the HISS-scoring system for estimation of trauma severity and the time off work after hand injuries].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2005 Aug;37(4):238-44. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-865800. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2005. PMID: 16149032 German.
-
Hand injury costs.Injury. 2006 Nov;37(11):1071-7. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2006.07.023. Epub 2006 Oct 12. Injury. 2006. PMID: 17045996 Review.
-
Current guidelines for management of severe hand injuries.Pol Orthop Traumatol. 2014 Jun 18;79:82-7. Pol Orthop Traumatol. 2014. PMID: 24941121 Review.
Cited by
-
An Anatomical Template for the Normalization of Medical Images of Adult Human Hands.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;13(12):2010. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13122010. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370905 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cinnamon Oil: Chemical Composition, Pharmacological Actions, and Applications.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 17;17(12):1700. doi: 10.3390/ph17121700. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39770541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Occupational Hand-Related Injuries at a Major Tertiary Care Burn and Reconstructive Center in Pakistan.Cureus. 2020 Sep 14;12(9):e10444. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10444. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33072454 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of complex hand injuries treated in the Plastic Surgery Department of a tertiary referral hospital in Warsaw.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021 Oct;47(5):1607-1612. doi: 10.1007/s00068-020-01312-5. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2021. PMID: 32025767 Free PMC article.
-
Echinacoside protects adenine-induced uremic rats from sciatic nerve damage by up-regulating α-Klotho.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2021 Sep 1;21(3):413-421. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2021. PMID: 34465681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hill C, Riaz M, Mozzam A, Brennen MD. A regional audit of hand and wrist injuries. A study of 4873 injuries. J Hand Surg Br. 1998;23:196–200. - PubMed
-
- Rosberg HE, Carlsson KS, Hojgard S, Lindgren B, Lundborg G, Dahlin LB. Injury to the human median and ulnar nerves in the forearm–analysis of costs for treatment and rehabilitation of 69 patients in southern Sweden. J Hand Surg Br. 2005;30:35–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

