Global regulation of promoter melting in naive lymphocytes
- PMID: 23706737
- PMCID: PMC3684982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.033
Global regulation of promoter melting in naive lymphocytes
Abstract
Lymphocyte activation is initiated by a global increase in messenger RNA synthesis. However, the mechanisms driving transcriptome amplification during the immune response are unknown. By monitoring single-stranded DNA genome wide, we show that the genome of naive cells is poised for rapid activation. In G0, ∼90% of promoters from genes to be expressed in cycling lymphocytes are polymerase loaded but unmelted and support only basal transcription. Furthermore, the transition from abortive to productive elongation is kinetically limiting, causing polymerases to accumulate nearer to transcription start sites. Resting lymphocytes also limit the expression of the transcription factor IIH complex, including XPB and XPD helicases involved in promoter melting and open complex extension. To date, two rate-limiting steps have been shown to control global gene expression in eukaryotes: preinitiation complex assembly and polymerase pausing. Our studies identify promoter melting as a third key regulatory step and propose that this mechanism ensures a prompt lymphocyte response to invading pathogens.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
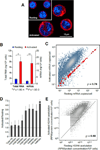
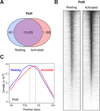

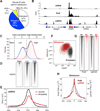
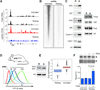
Comment in
-
Transitions for regulating early transcription.Cell. 2013 May 23;153(5):943-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.050. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23706732
References
-
- Benham CJ, Bi C. The analysis of stress-induced duplex destabilization in long genomic DNA sequences. J Comput Biol. 2004;11:519–543. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL, Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986;321:702–706. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

