Inflammasome-mediated pyroptotic and apoptotic cell death, and defense against infection
- PMID: 23707339
- PMCID: PMC3742712
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2013.04.004
Inflammasome-mediated pyroptotic and apoptotic cell death, and defense against infection
Abstract
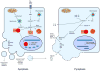
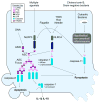
Cell death is an effective strategy to limit intracellular infections. Canonical inflammasomes, including NLRP3, NLRC4, and AIM2, recruit and activate caspase-1 in response to a range of microbial stimuli and endogenous danger signals. Caspase-1 then promotes the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 and a rapid form of lytic programmed cell death termed pyroptosis. A second inflammatory caspase, mouse caspase-11, mediates pyroptotic death through an unknown non-canonical inflammasome system in response to cytosolic bacteria. In addition, recent work shows that inflammasomes can also recruit procaspase-8, initiating apoptosis. The induction of multiple pathways of cell death has probably evolved to counteract microbial evasion of cell death pathways.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Angosto D, López-Castejón G, López-Muñoz A, Sepulcre MP, Arizcun M, Meseguer J, Mulero V. Evolution of inflammasome functions in vertebrates: Inflammasome and caspase-1 trigger fish macrophage cell death but are dispensable for the processing of IL-1β. Innate Immunity. 2012;18:815–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

