The transcriptional architecture of early human hematopoiesis identifies multilevel control of lymphoid commitment
- PMID: 23708252
- PMCID: PMC4961471
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2615
The transcriptional architecture of early human hematopoiesis identifies multilevel control of lymphoid commitment
Abstract
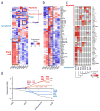
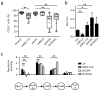
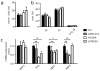
Understanding how differentiation programs originate from the gene-expression 'landscape' of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) is crucial for the development of new clinical therapies. We mapped the transcriptional dynamics underlying the first steps of commitment by tracking transcriptome changes in human HSCs and eight early progenitor populations. We found that transcriptional programs were extensively shared, extended across lineage-potential boundaries and were not strictly lineage affiliated. Elements of stem, lymphoid and myeloid programs were retained in multilymphoid progenitors (MLPs), which reflected a hybrid transcriptional state. By functional single cell analysis, we found that the transcription factors Bcl-11A, Sox4 and TEAD1 (TEF1) governed transcriptional networks in MLPs, which led to B cell specification. Overall, we found that integrated transcriptome approaches can be used to identify previously unknown regulators of multipotency and show additional complexity in lymphoid commitment.
Figures



References
-
- Enver T, Pera M, Peterson C, Andrews PW. Stem Cell States, Fates, and the Rules of Attraction. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4:387–397. - PubMed
-
- Zandi S, Bryder D, Sigvardsson M. Load and lock: the molecular mechanisms of B-lymphocyte commitment. Immunol Rev. 2010;238:47–62. - PubMed
-
- Nutt SL, Kee BL. The transcriptional regulation of B cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2007;26:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Georgopoulos K. Haematopoietic cell-fate decisions, chromatin regulation and ikaros. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:162–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

