Interfacial properties of high-density lipoprotein-like lipid droplets with different lipid and apolipoprotein A-I compositions
- PMID: 23708359
- PMCID: PMC3660637
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.02.058
Interfacial properties of high-density lipoprotein-like lipid droplets with different lipid and apolipoprotein A-I compositions
Abstract
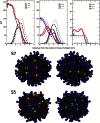
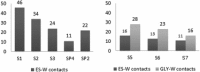
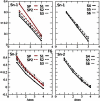
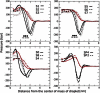
The surface properties of high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) are important because different enzymes bind and carry out their functions at the surface of HDL particles during metabolic processes. However, the surface properties of HDL and other lipoproteins are poorly known because they cannot be directly measured for nanoscale particles with contemporary experimental methods. In this work, we carried out coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations to study the concentration of core lipids in the surface monolayer and the interfacial tension of droplets resembling HDL particles. We simulated lipid droplets composed of different amounts of phospholipids, cholesterol esters (CEs), triglycerides (TGs), and apolipoprotein A-Is. Our results reveal that the amount of TGs in the vicinity of water molecules in the phospholipid monolayer is 25-50% higher compared to the amount of CEs in a lipid droplet with a mixed core of an equal amount of TG and CE. In addition, the correlation time for the exchange of molecules between the core and the monolayer is significantly longer for TGs compared to CEs. This suggests that the chemical potential of TG is lower in the vicinity of aqueous phase but the free-energy barrier for the translocation between the monolayer and the core is higher compared to CEs. From the point of view of enzymatic modification, this indicates that TG molecules are more accessible from the aqueous phase. Further, our results point out that CE molecules decrease the interfacial tension of HDL-like lipid droplets whereas TG keeps it constant while the amount of phospholipids varies.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computational studies of plasma lipoprotein lipids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Oct;1858(10):2401-2420. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26969087
-
Role of lipids in spheroidal high density lipoproteins.PLoS Comput Biol. 2010 Oct 28;6(10):e1000964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000964. PLoS Comput Biol. 2010. PMID: 21060857 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsideration of hydrophobic lipid distributions in lipoprotein particles.Chem Phys Lipids. 2008 Sep;155(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2008.06.003. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Chem Phys Lipids. 2008. PMID: 18611396
-
Structure of apo A-I high-density lipoproteins: a review.Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997 Jan;62(1):1-14. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997. PMID: 9113723 Review.
-
Formation and metabolism of prebeta-migrating, lipid-poor apolipoprotein A-I.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004 Mar;24(3):421-8. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000104029.74961.f5. Epub 2003 Oct 30. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004. PMID: 14592845 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular dynamics simulations of lipid nanodiscs.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Oct;1860(10):2094-2107. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.04.015. Epub 2018 May 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29729280 Free PMC article.
-
Study of trioleoylglycerol two-layer and adiposome cross-section mimicking four-layer systems through atomic-level simulations.Struct Dyn. 2022 Dec 5;9(6):064701. doi: 10.1063/4.0000168. eCollection 2022 Nov. Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 36484071 Free PMC article.
-
Interdigitation between Triglycerides and Lipids Modulates Surface Properties of Lipid Droplets.Biophys J. 2017 Apr 11;112(7):1417-1430. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.02.032. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28402884 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic Acid Supplementation Increases HDL Content in n-3 Fatty Acids and Improves Endothelial Function in Hypertriglyceridemic Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 11;24(6):5390. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065390. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982461 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Surface and Hydration Properties of Lipid Droplets.Biophys J. 2020 Nov 17;119(10):1958-1969. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 33120015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lund-Katz S., Liu L., Phillips M.C. High density lipoprotein structure. Front. Biosci. 2003;8:d1044–d1054. - PubMed
-
- Tsompanidi E.M., Brinkmeier M.S., Kypreos K.E. HDL biogenesis and functions: role of HDL quality and quantity in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2010;208:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Mahley R.W., Innerarity T.L., Weisgraber K.H. Plasma lipoproteins: apolipoprotein structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 1984;25:1277–1294. - PubMed
-
- Ibdah J.A., Krebs K.E., Phillips M.C. The surface properties of apolipoproteins A-I and A-II at the lipid/water interface. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1989;1004:300–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

