Caloric restriction augments radiation efficacy in breast cancer
- PMID: 23708519
- PMCID: PMC3735710
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.25016
Caloric restriction augments radiation efficacy in breast cancer
Abstract
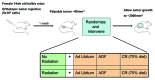
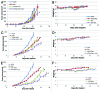
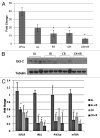
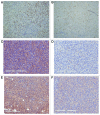
Dietary modification such as caloric restriction (CR) has been shown to decrease tumor initiation and progression. We sought to determine if nutrient restriction could be used as a novel therapeutic intervention to enhance cytotoxic therapies such as radiation (IR) and alter the molecular profile of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which displays a poor prognosis. In two murine models of TNBC, significant tumor regression is noted with IR or diet modification, and a greater regression is observed combining diet modification with IR. Two methods of diet modification were compared, and it was found that a daily 30% reduction in total calories provided more significant tumor regression than alternate day feeding. At the molecular level, tumors treated with CR and IR showed less proliferation and more apoptosis. cDNA array analysis demonstrated the IGF-1R pathway plays a key role in achieving this physiologic response, and multiple members of the IGF-1R pathway including IGF-1R, IRS, PIK3ca and mTOR were found to be downregulated. The innovative use of CR as a novel therapeutic option has the potential to change the biology of tumors and enhance the opportunity for clinical benefit in the treatment of patients with TNBC.
Keywords: IGF; breast cancer; caloric restriction; cytotoxic therapy; radiation; tumor regression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caloric restriction coupled with radiation decreases metastatic burden in triple negative breast cancer.Cell Cycle. 2016 Sep;15(17):2265-74. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1160982. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Cell Cycle. 2016. PMID: 27027731 Free PMC article.
-
Caloric restriction counteracts chemotherapy-induced inflammation and increases response to therapy in a triple negative breast cancer model.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(13):1536-1544. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1471314. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 29912618 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Targeting IGF-1R and Autophagy Enhances the Effects of Cell Growth Suppression and Apoptosis Induced by the IGF-1R Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 3;12(1):e0169229. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169229. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28046018 Free PMC article.
-
Role of estrogen receptor alpha in modulating IGF-I receptor signaling and function in breast cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Sep;23(3):385-94. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15595626 Review.
-
Roles for insulin-like growth factor-1 in mediating the anti-carcinogenic effects of caloric restriction.J Nutr Health Aging. 1999;3(2):92-101. J Nutr Health Aging. 1999. PMID: 10885804 Review.
Cited by
-
Calorie Restriction and Time-Restricted Feeding: Effective Interventions in Overweight or Obese Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy Treatment with Curative Intent for Cancer.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 7;16(4):477. doi: 10.3390/nu16040477. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398802 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Attacking the supply wagons to starve cancer cells to death.FEBS Lett. 2016 Apr;590(7):885-907. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12121. Epub 2016 Mar 22. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 26938658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer.Cell Res. 2018 Mar;28(3):265-280. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.155. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 29219147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspective: Do Fasting, Caloric Restriction, and Diets Increase Sensitivity to Radiotherapy? A Literature Review.Adv Nutr. 2020 Sep 1;11(5):1089-1101. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa062. Adv Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32492154 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Interventions Targeting Gut Microbiota during Cancer Therapies.Microorganisms. 2021 Jul 9;9(7):1469. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9071469. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34361904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
