Anti-oxidative and cholesterol efflux capacities of high-density lipoprotein are reduced in ischaemic cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 23709232
- PMCID: PMC3888304
- DOI: 10.1093/eurjhf/hft084
Anti-oxidative and cholesterol efflux capacities of high-density lipoprotein are reduced in ischaemic cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Aims: Various pathological changes lead to the development of heart failure (HF). HDL is dysfunctional in both acute coronary syndrome, as measured by the HDL inflammatory index (HII) assay, and stable coronary disease, as measured by cholesterol efflux capacity. We therefore hypothesized that these functions of HDL are also impaired in subjects with ischaemic cardiomyopathy.
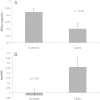
Methods and results: A case-control study was performed on subjects in the University of Pennsylvania Catheterization Study (PennCath) cohort of patients with angina. Cases had EF <50% and angiographic CAD (≥70% stenosis of any vessel; n = 23); controls included those with EF ≥55% and no CAD (n = 46). Serum from subjects was apolipoprotein-B depleted to isolate an HDL fraction. To measure HDL anti-oxidative capacity, the HDL fraction was incubated with LDL and a reporter lipid that fluoresces when oxidized. To measure cholesterol efflux capacity, the HDL fraction was also incubated with macrophages and tritium-labelled cholesterol. Mean HII was higher and efflux capacity lower in subjects with ischaemic cardiomyopathy (HII 0.26 vs. -0.028; efflux 0.80 vs. 0.92; P < 0.05). In a multivariable logistic regression model, both high HII and low efflux capacity were significant risk factors for HF [HII odds ratio (OR) 2.8, 95% confidence interval (CI) 2.0-3.9, P = 0.002; efflux OR 2.1, 95% CI 1.5-3.0, P = 0.03]. These effects persisted after adjustment for covariates and traditional risk factors for HF.
Conclusion: Subjects with reduced EF from ischaemia have lower HDL concentration and also impaired HDL function. HDL is a versatile lipoprotein particle with various anti-inflammatory and vasoprotective functions, whose impairment may contribute to ischaemic heart failure.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; HDL cholesterol; Heart failure.
Figures
References
-
- Holme I, Strandberg TE, Faergeman O, Kastelein JJ, Olsson AG, Tikkanen MJ, Larsen ML, Lindahl C, Pedersen TR Incremental Decrease in End Points Through Aggressive Lipid Lowering Study Group. Congestive heart failure is associated with lipoprotein components in statin-treated patients with coronary heart disease Insights from the Incremental Decrease in End points Through Aggressive Lipid Lowering Trial (IDEAL) Atherosclerosis. 2009;205:522–527. - PubMed
-
- Aronow WS, Ahn C. Frequency of congestive heart failure in older persons with prior myocardial infarction and serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol>or=125 mg/dl treated with statins versus no lipid-lowering drug. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:147–149. - PubMed
-
- Freitas HF, Barbosa EA, Rosa FH, Lima AC, Mansur AJ. Association of HDL cholesterol and triglycerides with mortality in patients with heart failure. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2009;42:420–425. - PubMed
-
- Mehra MR, Uber PA, Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Park MH, Ventura HO. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and prognosis in advanced heart failure. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2009;28:876–880. - PubMed
-
- Christ M, Klima T, Grimm W, Mueller HH, Maisch B. Prognostic significance of serum cholesterol levels in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:691–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

