Telemonitoring based service redesign for the management of uncontrolled hypertension: multicentre randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 23709583
- PMCID: PMC3663293
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f3030
Telemonitoring based service redesign for the management of uncontrolled hypertension: multicentre randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Objective: To determine if an intervention consisting of telemonitoring and supervision by usual primary care clinicians of home self measured blood pressure and optional patient decision support leads to clinically important reductions in daytime systolic and diastolic ambulatory blood pressure in patients with uncontrolled blood pressure.
Design: Multicentre randomised controlled trial.
Setting: 20 primary care practices in south east Scotland.
Participants: 401 people aged 29-95 years with uncontrolled blood pressure (mean daytime ambulatory measurement ≥ 135/85 mm Hg but ≤ 210/135 mm Hg).
Intervention: Self measurement and transmission of blood pressure readings to a secure website for review by the attending nurse or doctor and participant, with optional automated patient decision support by text or email for six months.
Main outcome measures: Blinded assessment of mean daytime systolic ambulatory blood pressure six months after randomisation.
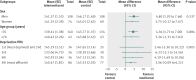
Results: 200 participants were randomised to the intervention and 201 to usual care; primary outcome data were available for 90% of participants (182 and 177, respectively). The mean difference in daytime systolic ambulatory blood pressure adjusted for baseline and minimisation factors between intervention and usual care was 4.3 mm Hg (95% confidence interval 2.0 to 6.5; P=0.0002) and for daytime diastolic ambulatory blood pressure was 2.3 mm Hg (0.9 to 3.6; P=0.001), with higher values in the usual care group. The intervention was associated with a mean increase of one general practitioner (95% confidence interval 0.5 to 1.6; P=0.0002) and 0.6 (0.1 to 1.0; P=0.01) practice nurse consultations during the course of the study.
Conclusions: Supported self monitoring by telemonitoring is an effective method for achieving clinically important reductions in blood pressure in patients with uncontrolled hypertension in primary care settings. However, it was associated with increase in use of National Health Service resources. Further research is required to determine if the reduction in blood pressure is maintained in the longer term and if the intervention is cost effective.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN72614272.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
References
-
- Lawes CMM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A, for the International Society of Hypertension, et al. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 2008;371:1513-8. - PubMed
-
- Pickering TG, Miller NH, Ogedegbe G, Krakoff LR, Artinian NT, Goff D. Call to action on use and reimbursement for home blood pressure monitoring: a joint scientific statement from the American Heart Association, American Society of Hypertension, and Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association. Hypertension 2008;52:10-29. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Okonofua EC, Simpson KN, Jesri A, Rehman SU, Durlkalski VL, Egan BM. Therapeutic inertia is an impediment to achieving the healthy people 2010 blood pressure control goals. Hypertension 2006;47:345-51. - PubMed
-
- Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med 2005;353:487-97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical