High-fat feeding rapidly induces obesity and lipid derangements in C57BL/6N mice
- PMID: 23712496
- PMCID: PMC3685703
- DOI: 10.1007/s00335-013-9456-0
High-fat feeding rapidly induces obesity and lipid derangements in C57BL/6N mice
Abstract
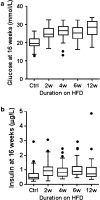
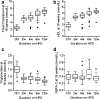
C57BL/6N (B6N) is becoming the standard background for genetic manipulation of the mouse genome. The B6N, whose genome is very closely related to the reference C57BL/6J genome, is versatile in a wide range of phenotyping and experimental settings and large repositories of B6N ES cells have been developed. Here, we present a series of studies showing the baseline characteristics of B6N fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for up to 12 weeks. We show that HFD-fed B6N mice show increased weight gain, fat mass, and hypercholesterolemia compared to control diet-fed mice. In addition, HFD-fed B6N mice display a rapid onset of lipid accumulation in the liver with both macro- and microvacuolation, which became more severe with increasing duration of HFD. Our results suggest that the B6N mouse strain is a versatile background for studying diet-induced metabolic syndrome and may also represent a model for early nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures



References
-
- Armbruster DA. Fructosamine: structure, analysis, and clinical usefulness. Clin Chem. 1987;33:2153–2163. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi C, Monetal D, Brughera M, Salvo M, Lamparelli D, Mazué G, Iatropoulos MJ. Haematology and clinical chemistry in rats: comparison of different blood collection sites. Comp Haematol Int. 1996;6:160–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00368460. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

