Prevalence and estimation of hepatitis B and C infections in the WHO European Region: a review of data focusing on the countries outside the European Union and the European Free Trade Association
- PMID: 23714072
- PMCID: PMC3891474
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268813000940
Prevalence and estimation of hepatitis B and C infections in the WHO European Region: a review of data focusing on the countries outside the European Union and the European Free Trade Association
Abstract
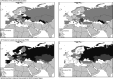
Knowledge of hepatitis B and C prevalence, and numbers infected, are important for planning responses. Published HBsAg and anti-HCV prevalences for the 20 WHO European Region countries outside the EU/EFTA were extracted, to complement published data for the EU/EFTA. The general population prevalence of HBsAg (median 3·8%, mean 5·0%, seven countries) ranged from 1·3% (Ukraine) to 13% (Uzbekistan), and anti-HCV (median 2·3%, mean 3·8%, 10 countries) from 0·5% (Serbia, Tajikistan) to 13% (Uzbekistan). People who inject drugs had the highest prevalence of both infections (HBsAg: median 6·8%, mean 8·2%, 13 countries; anti-HCV: median 46%, mean 46%, 17 countries), and prevalence was also elevated in men who have sex with men and sex workers. Simple estimates indicated 13·3 million (1·8%) adults have HBsAg and 15·0 million (2·0%) HCV RNA in the WHO European Region; prevalences were higher outside the EU/EFTA countries. Efforts to prevent, diagnose, and treat these infections need to be maintained and improved. This article may not be reprinted or reused in any way in order to promote any commercial products or services.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Prevention and control of viral hepatitis infection: frame work for global action 2012. Geneva: WHO, 2012. (www.who.int/csr/disease/hepatitis/GHP_framework.pdf). Accessed 14 December 2012.
-
- Lavanchy D. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology, disease burden, treatment, and current and emerging prevention and control measures. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 2004; 11: 97–107. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein ST, et al. A mathematical model to estimate global hepatitis B disease burden and vaccination impact. International Journal of Epidemiology 2005; 34: 1329–39. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis C – global prevalence (update). Weekly Epidemiological Record 1999; 74: 425–27.
-
- WHO Executive Board. Viral hepatitis. Report by the Secretariat. EB126/15. Geneva: WHO; 12 November 2009: http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB126/B126_15-en.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical