Immune thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 23714309
- PMCID: PMC3672858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.hoc.2013.03.001
Immune thrombocytopenia
Abstract
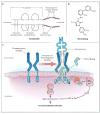
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a common hematologic disorder characterized by isolated thrombocytopenia. ITP presents as a primary or a secondary form. ITP may affect individuals of all ages, with peaks during childhood and in the elderly, in whom the age-specific incidence of ITP is greatest. Bleeding is the most common clinical manifestation of ITP. The pathogenesis of ITP is complex, involving alterations in humoral and cellular immunity. Corticosteroids remain the most common first line therapy for ITP. This article summarizes the classification and diagnosis of primary and secondary ITP, as well as the pathogenesis and options for treatment.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Rodeghiero F, Stasi R, Gernsheimer T, et al. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: report from an international working group. Blood. 2009;113:2386–2393. - PubMed
-
- Stasi R, Newland AC. ITP: a historical perspective. Br J Haematol. 2011;153(4):437–450. - PubMed
-
- Cuker A, Cines DB. Immune thrombocytopenia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2010;2010:377–84. - PubMed
-
- Semple JW, Provan D, Garvey MB, Freedman J. Recent progress in understanding the pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopenia. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(6):590–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

