Tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPA) as a membrane-permeable chelator for interception of biological mobile zinc
- PMID: 23715510
- PMCID: PMC3730853
- DOI: 10.1039/c3mt00103b
Tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPA) as a membrane-permeable chelator for interception of biological mobile zinc
Abstract
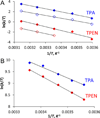
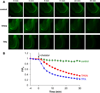
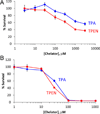
We report the characterization of tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPA) as a membrane-permeable zinc chelator for intercepting biological mobile zinc. Compared to N,N,N',N'-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine (TPEN), TPA chelates zinc with faster kinetics in cuvettes, live cells, and brain slices. TPA also is generally less toxic than TPEN in cell culture. Mechanistic analysis indicates that these improvements arise from both the electronic and steric properties of TPA including weaker metal-binding affinity, lower pKa, and smaller size. These results demonstrate that TPA chelation is a valuable addition to the methodologies available for investigating mobile zinc in biology.
Figures





References
-
- Maret W. BioMetals. 2009;22:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Vallee BL, Falchuk KH. Physiol. Rev. 1993;73:79–118. - PubMed
-
- Chang CJ, Lippard SJ. Neurodegenerative Diseases and Metal Ions. John Wiley & Sons; 2006. pp. 321–370.
-
- Sensi SL, Paoletti P, Bush AI, Sekler I. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009;10:780–791. - PubMed
-
- Taylor CG. BioMetals. 2005;18:305–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

