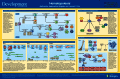
Hematopoiesis
- PMID: 23715539
- PMCID: PMC3666375
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.083147
Hematopoiesis
Abstract
Hematopoiesis - the process by which blood cells are formed - has been studied intensely for over a century using a variety of model systems. There is conservation of the overall hematopoietic process between vertebrates, although some differences do exist. Over the last decade, the zebrafish has come to the forefront as a new model in hematopoiesis research, as it allows the use of large-scale genetics, chemical screens and transgenics. This comparative approach to understanding hematopoiesis has led to fundamental knowledge about the process and to the development of new therapies for disease. Here, we provide a broad overview of vertebrate hematopoiesis. We also highlight the benefits of using zebrafish as a model.
Keywords: Hematopoiesis; Mouse; Zebrafish.
References
-
- Adamo L., García-Cardeña G. (2012). The vascular origin of hematopoietic cells. Dev. Biol. 362, 1-10 - PubMed
-
- Burns C. E., DeBlasio T., Zhou Y., Zhang J., Zon L., Nimer S. D. (2002). Isolation and characterization of runxa and runxb, zebrafish members of the runt family of transcriptional regulators. Exp. Hematol. 30, 1381-1389 - PubMed
-
- Calvi L. M., Adams G. B., Weibrecht K. W., Weber J. M., Olson D. P., Knight M. C., Martin R. P., Schipani E., Divieti P., Bringhurst F. R., et al. (2003). Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature 425, 841-846 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases