Lenalidomide, melphalan and dexamethasone in a population of patients with immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis with high rates of advanced cardiac involvement
- PMID: 23716538
- PMCID: PMC3789465
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.084574
Lenalidomide, melphalan and dexamethasone in a population of patients with immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis with high rates of advanced cardiac involvement
Abstract
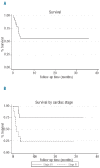
Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis remains incurable despite recent therapeutic advances, and is particularly difficult to treat in patients with amyloid cardiomyopathy. Based on evidence of activity in multiple myeloma, we designed a pilot study of an oral regimen of lenalidomide in combination with dexamethasone and low-dose melphalan in order to evaluate its safety and efficacy in patients with amyloidosis, including those with advanced cardiac involvement. Twenty-five patients were enrolled. Ninety-two percent of patients had cardiac involvement by amyloidosis, and 36% of patients met the criteria for Mayo Clinic cardiac stage III disease. Patients received up to nine cycles of treatment, consisting of lenalidomide 10 mg/day orally on days 1 - 21 (28-day cycle); melphalan 0.18 mg/kg orally on days 1-4; and dexamethasone 40 mg orally on days 1, 8, 15, and 22. High rates (33%) of cardiac arrhythmias and low rates of treatment completion (12.5%) were observed. Ten patients died during the study, all within the first several months of treatment due to acute cardiac events. The overall hematologic response rate was 58%, however organ responses were seen in only 8% of patients. The overall survival rate at 1 year was 58%. While we confirmed the hematologic response rates observed with similar regimens, front-line treatment with melphalan, lenalidomide and dexamethasone was toxic, ineffective, and did not alter survival outcomes for patients with high-risk cardiac disease. Our data highlight the importance of developing novel treatment approaches for amyloid cardiomyopathy. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00890552).
Figures
References
-
- Merlini G, Bellotti V. Molecular mechanisms of amyloidosis. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349(6):583–96 - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Greipp PR, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ, et al. A trial of three regimens for primary amyloidosis: colchicine alone, melphalan and prednisone and melphalan, prednisone and colchicine. N Engl J Med. 1997;336(17):1202–7 - PubMed
-
- Comenzo RL, Reece D, Palladini G, Seldin D, Sanchorawala V, Landau H, et al. Consensus guidelines for the conduct and reporting of clinical trials in systemic light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. Leukemia. 2012; 26(11):2317–25 - PubMed
-
- Skinner M, Anderson J, Simms R, Falk R, Wang M, Libbey C, et al. Treatment of 100 patients with primary amyloidosis: a randomized trial of melphalan, prednisone, and colchicines versus colchicine only. Am J Med. 1996;100(3):290–8 - PubMed
-
- Palladini G, Perfetti V, Obici L, Caccialanza R, Semio A, Adami F, et al. Association of melphalan and high-dose dexamethasone is effective and well-tolerated in patients with AL (primary) amyloidosis who are ineligible for stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2004;103(8):2936–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous