A novel orally available inhibitor of focal adhesion signaling increases survival in a xenograft model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with central nervous system involvement
- PMID: 23716554
- PMCID: PMC3729905
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2012.071811
A novel orally available inhibitor of focal adhesion signaling increases survival in a xenograft model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with central nervous system involvement
Abstract
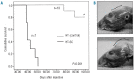
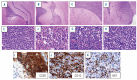
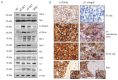
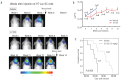
Central nervous system dissemination is a relatively uncommon but almost always fatal complication in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Optimal therapy for central nervous involvement in this malignancy has not been established. In this paper, we aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect of E7123, a celecoxib derivative that inhibits focal adhesion signaling, in a novel xenograft model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with central nervous system involvement. Cells obtained after disaggregation of HT subcutaneous tumors (HT-SC cells) were intravenously injected in NOD/SCID mice. These mice received oral vehicle or 75 mg/kg of E7123 daily until they were euthanized for weight loss or signs of sickness. The antitumor effect of E7123 was validated in an independent experiment using a bioluminescent mouse model. Intravenously injected HT-SC cells showed higher take rate and higher central nervous system tropism (associated with increased expression of β1-integrin and p130Cas proteins) than HT cells. The oral administration of E7123 significantly increased survival time in 2 independent experiments using mice injected with unmodified or bioluminescent HT-SC cells. We have developed a new xenograft model of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with central nervous system involvement that can be used in the pre-clinical evaluation of new drugs for this malignancy. E7123 is a new, well-tolerated and orally available therapeutic agent that merits further investigation since it may improve current management of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with central nervous system involvement.
Figures
References
-
- Korfel A. Prevention of central nervous system relapses in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: which patients and how? Curr Opin Oncol. 2011;23(5):436–40 - PubMed
-
- Tai WM, Chung J, Tang PL, Koo YX, Hou X, Tay KW, et al. Central nervous system (CNS) relapse in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL): pre- and post-rituximab. Ann Hematol. 2011;90(7):809–18 - PubMed
-
- van Besien K, Ha CS, Murphy S, McLaughlin P, Rodriguez A, Amin K, et al. Risk factors, treatment, and outcome of central nervous system recurrence in adults with intermediate-grade and immunoblastic lymphoma. Blood. 1998;91(4):1178–84 - PubMed
-
- Hollender A, Kvaloy S, Lote K, Nome O, Holte H. Prognostic factors in 140 adult patients with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with systemic central nervous system (CNS) involvement. A single centre analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2000;36(14):1762–8 - PubMed
-
- Gleissner B, Chamberlain M. Treatment of CNS dissemination in systemic lymphoma. J Neurooncol. 2007;84(1):107–17 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

