A novel 11;18 translocation in a case of acute myeloid leukemia with maturation
- PMID: 23716952
- PMCID: PMC3656533
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6866.108050
A novel 11;18 translocation in a case of acute myeloid leukemia with maturation
Abstract
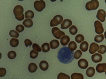
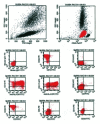
Acute myeloid leukemia with maturation (AML-M2) is associated with the 8;21 translocation. For the first time in an adult patient with AML-M2, a novel unbalanced translocation involving the short arm of chromosome 11 and long arm of chromosome18 with new breakpoints is presented. CD82 on band 11p11.2 and GATA 6 on 18q11.2 may play a role in the pathogenesis of de novo AML M2. The report with translocation (11;18)(p11.2;q11.2), as the sole cytogenetic abnormality provides more data on the leukemogenesis of de novo AML M2.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia with maturation 2; CD82; GATA6; chromosomal abnormality; immunophenotyping; translocation 11;18.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

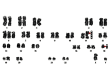
References
-
- Raimondi SC. Cytogenetics of Acute Leukemias. In: Ching-Hon Pui., editor. Childhood Leukemias. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2006. pp. 235–71.
-
- Ross JA. Epidemiology and Hereditary aspects of Acute leukemia. In: Wiernik PH, Goldman JM, Dulcher JP, Kyle RA, editors. Neoplastic diseases of the blood. 4th ed. Cambridge: Press syndicate of University of Cambridge; 2003. pp. 164–75.
-
- Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber AD, Brunning RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114:937–51. - PubMed
-
- Naeim Faramarz, Rao PN. Acute myeloid Leukemia. In: Naeim F, Rao PN, Grody WW, editors. Hematopathology Morphology, Immunophenotype, Cytogenetics, And Molecular Approaches. 1st ed. Amsterdam: UK Academic press- Elsevier; 2008. pp. 207–55.
-
- Krzysztof M, Bloomfield CD. Clinical significance of most common chromosome translocations in acute myeloid leukemia. J Natl Inst Monogr. 2008;39:52–57. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

