Robotic cholecystectomy with new port sites
- PMID: 23716987
- PMCID: PMC3662947
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i20.3077
Robotic cholecystectomy with new port sites
Abstract
Aim: To introduce robotic cholecystectomy (RC) using new port sites on the low abdominal area.
Methods: From June 2010 to June 2011, a total of 178 RCs were performed at Ajou University Medical Center. We prospectively collected the set-up time (working time and docking time) and console time in all robotic procedures.
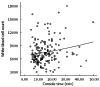
Results: Eighty-three patients were male and 95 female; the age ranged from 18 to 72 years of age (mean 54.6 ± 15.0 years). All robotic procedures were successfully completed. The mean operation time was 52.4 ± 17.1 min. The set-up time and console time were 11.9 ± 5.4 min (5-43 min) and 15.1 ± 8.0 min (4-50 min), respectively. The conversion rate to laparoscopic or open procedures was zero. The complication rate was 0.6% (n = 1, bleeding). There was no bile duct injury or mortality. The mean hospital stay was 1.4 ± 1.1 d. There was a significant correlation between the console time and white blood cell count (r = 0.033, P = 0.015). In addition, the higher the white blood cell count (more than 10000), the longer the console time.
Conclusion: Robotic cholecystectomy using new port sites on the low abdominal area can be safely and efficiently performed, with sufficient patient satisfaction.
Keywords: Abdominal area; Gallbladder disease; Operation time; Port sites; Robotic cholecystectomy.
Figures

References
-
- Brasesco OE, Rosin D, Rosenthal RJ. Laparoscopic surgery of the liver and biliary tract. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2002;12:91–100. - PubMed
-
- Voitk AJ, Tsao SG, Ignatius S. The tail of the learning curve for laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Am J Surg. 2001;182:250–253. - PubMed
-
- Dakin GF, Gagner M. Comparison of laparoscopic skills performance between standard instruments and two surgical robotic systems. Surg Endosc. 2003;17:574–579. - PubMed
-
- Jourdan IC, Dutson E, Garcia A, Vleugels T, Leroy J, Mutter D, Marescaux J. Stereoscopic vision provides a significant advantage for precision robotic laparoscopy. Br J Surg. 2004;91:879–885. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

