Comparison of Ginsenoside and Phenolic Ingredient Contents in Hydroponically-cultivated Ginseng Leaves, Fruits, and Roots
- PMID: 23717146
- PMCID: PMC3659603
- DOI: 10.5142/jgr.2012.36.4.425
Comparison of Ginsenoside and Phenolic Ingredient Contents in Hydroponically-cultivated Ginseng Leaves, Fruits, and Roots
Abstract
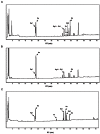
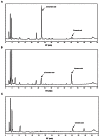
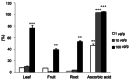
In this study, hydroponically-cultivated ginseng leaves, fruits, and roots were respectively extracted with ethanol. The contents of 12 ginsenosides and three phenolics in the extracts were quantitatively analyzed and the free radical scavenging activities were measured and compared. Hydroponically-cultivated ginseng leaves contained higher levels of gensenosides (Rg1, Rg2+Rh1, Rd, and Rg3) and p-coumaric acid than the other parts of the ginseng plants. The 2,2'-azino-di-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline)-6-sulfonic acid radical scavenging activities of leaves were also the highest. Accordingly, hydroponically-grown ginseng leaves were shown to hold promise for use as an environmentally-friendly natural anti-oxidant.
Keywords: Ginsenoside; Hydroponic cultivation; Leaves; Panax ginseng; Phenolic compound.
Figures
References
-
- Park JD. Recent studies on the chemical constituents of Korean ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer). Korean J Ginseng Sci. 1996;20:389–415.
-
- Lee DY, Cho JG, Lee MK, Lee JW, Lee YH, Yang DC, Baek NI. Discrimination of Panax ginseng roots cultivated in different areas in Korea using HPLC-ELSD and principal component analysis. J Ginseng Res. 2011;35:31–38. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2011.35.1.031. - DOI
-
- Kim HD, Ha SE, Kang JR, Park JK. Effect of Korean red ginseng extract on cell death responses in peroxynitrite-treated keratinocytes. J Ginseng Res. 2010;34:205–211.
-
- Hong HD, Sim EM, Kim KT, Rho JH, Rhee YK, Cho CW. Comparison of preparation methods for the quantification of ginsenosides in raw Korean ginseng. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2009;18:565–569.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
