Varied spectrum of clinical presentation and mortality in a prospective registry of visceral leishmaniasis in a low endemicity area of Northern Italy
- PMID: 23718708
- PMCID: PMC3674923
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-248
Varied spectrum of clinical presentation and mortality in a prospective registry of visceral leishmaniasis in a low endemicity area of Northern Italy
Abstract
Background: Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL) is endemic in 88 countries, in areas of relatively low incidence with a relevant proportion of immune suppressed patients clinical presentation, diagnosis and management may present difficulties and pitfalls.
Methods: Demographic data, clinical, laboratory features and therapeutic findings were recorded in patients identified by a regional VL disease registry from January 2007 to December 2010.
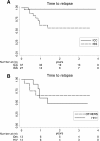
Results: A total of 55 patients (36 adults mean age 48.7 years, 19 children median age 37.5 months) were observed presenting with 65 episodes. All childen were immunocompetent, whereas adults affected by VL included both immunocompetent (n°17) and immunesuppressed (n°19) patients. The clinical presentation was homogeneous in children with predominance of fever and hepato-splenomegaly. A wider spectrum of clinical presentations was observed in immunocompromised adults. Bone marrow detection of intracellular parasites (Giemsa staining) and serology (IFAT) were the most frequently used diagnostic tools. In addition, detection of urinary antigen was used in adult patients with good specificity (90%). Liposomal amphotericin B was the most frequently prescribed first line drug (98.2% of cases) with 100% clinical cure. VL relapses (n°10) represented a crucial finding: they occurred only in adult patients, mainly in immunocompromised patients (40% of HIV, 22% of non-HIV immunocompromised patients, 5,9% of immunocompetent patients). Furthermore, three deaths with VL were reported, all occurring in relapsing immunocompromised patients accounting for a still high overall mortality in this group (15.8%).
Conclusions: The wide spectrum of clinical presentation in immunesuppresed patients and high recurrence rates still represent a clinical challenge accounting for high mortality. Early clinical identification and satisfactory treatment performance with liposomal amphotericin B are confirmed in areas with low-level endemicity and good clinical standards. VL needs continuing attention in endemic areas where increasing numbers of immunocompromised patients at risk are dwelling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Leishmaniasis in Sudan. Visceral leishmaniasis.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2001 Apr;95 Suppl 1:S27-58. doi: 10.1016/s0035-9203(01)90218-4. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2001. PMID: 11370250
-
Current clinical, laboratory, and treatment outcome characteristics of visceral leishmaniasis: results from a seven-year retrospective study in Greece.Int J Infect Dis. 2015 May;34:46-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2015.02.021. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Int J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25743761
-
Prognostic factors for death from visceral leishmaniasis in patients treated with liposomal amphotericin B in an endemic state in Brazil.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2017 Apr 1;111(4):163-171. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trx029. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2017. PMID: 28673017
-
[Change in human visceral leishmaniasis treatment in Italy: retrospective study of 630 patients].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):199-201. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305716 Review. Italian.
-
[Infantile visceral leishmaniasis in the Campania region, Italy: experience from a Paediatric Referral Centre].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):221-3. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305721 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and antileishmanial evaluation of some 2,3-disubstituted-4(3H)-quinazolinone derivatives.Org Med Chem Lett. 2014 Dec;4(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13588-014-0010-1. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Org Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 26548988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Report on Global Surveillance of Epidemic-prone Infectious Diseases. Chapter ten Leishmaniasis and Leishmania HIV/coinfection: Background Information. WHO; 2009. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/surveillance/Leishmaniasis... last accessed May 03rd 2012.
-
- Ready PD. In: Climate change: the impact on the epidemiology and control of animal diseases. de la Roque S, editor. Vol. 27. 2008. Leishmaniasis emergence and climate change; pp. 399–412. Rev Sci Tech Off Int Epiz.
-
- Hovius E, Pinelli E, Nijsse R, Poot J, van der Giessen J. Introduction of leishmania species in the Netherland from dogs who are returning from military missions and vacations in countries where leishmaniasis is endemic. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 2011;136:344–348. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

