Inequality in fertility rate and modern contraceptive use among Ghanaian women from 1988-2008
- PMID: 23718745
- PMCID: PMC3668986
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-9276-12-37
Inequality in fertility rate and modern contraceptive use among Ghanaian women from 1988-2008
Abstract
Background: In most resource poor countries, particularly sub-Saharan Africa, modern contraceptive use and prevalence is unusually low and fertility is very high resulting in rapid population growth and high maternal mortality and morbidity. Current evidence shows slow progress in expanding the use of contraceptives by women of low socioeconomic status and insufficient financial commitment to family planning programs. We examined gaps and trends in modern contraceptive use and fertility within different socio-demographic subgroups in Ghana between 1988 and 2008.
Methods: We constructed a database using the Women's Questionnaire from the Ghana Demographic and Health Survey (GDHS) 1988, 1993, 1998, 2003 and 2008. We applied regression-based Total Attributable Fraction (TAF); we also calculated the Relative and Slope Indices of Inequality (RII and SII) to complement the TAF in our investigation.
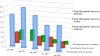
Results: Equality in use of modern contraceptives increased from 1988 to 2008. In contrast, inequality in fertility rate increased from 1988 to 2008. It was also found that rural-urban residence gap in the use of modern contraceptive methods had almost disappeared in 2008, while education and income related inequalities remained.
Conclusions: One obvious observation is that the discrepancy between equality in use of contraceptives and equality in fertility must be addressed in a future revision of policies related to family planning. Otherwise this could be a major obstacle for attaining further progress in achieving the Millennium Development Goal (MDG) 5. More research into the causes of the unfortunate discrepancy is urgently needed. There still exist significant education and income related inequalities in both parameters that need appropriate action.
Figures


References
-
- Boerma JT, Bryce J, Kinfu Y, Axelson H, Victora CG. Mind the gap: equity and trends in coverage of maternal, newborn, and child health services in 54 Countdown countries. Lancet. 2008;371(9620):1259–1267. - PubMed
-
- Lozano R, Wang H, Foreman KJ, Rajaratnam JK, Naghavi M, Marcus JR, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Lofgren KT, Phillips D, Atkinson C. Progress towards Millennium Development Goals 4 and 5 on maternal and child mortality: an updated systematic analysis. Lancet. 2011;378(9797):1139–1165. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61337-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nations U: Department of E, Social A. The millennium development goals report. 2010: 2010. New York: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs; 2010.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

