Tyrosine kinase inhibitors impair B-cell immune responses in CML through off-target inhibition of kinases important for cell signaling
- PMID: 23719297
- PMCID: PMC5726329
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-11-465039
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors impair B-cell immune responses in CML through off-target inhibition of kinases important for cell signaling
Abstract
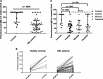
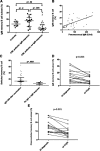
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have significant off-target multikinase inhibitory effects. We aimed to study the impact of TKIs on the in vivo B-cell response to vaccination. Cellular and humoral responses to influenza and pneumococcal vaccines were evaluated in 51 chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients on imatinib, or second-line dasatinib and nilotinib, and 24 controls. Following vaccination, CML patients on TKI had significant impairment of IgM humoral response to pneumococcus compared with controls (IgM titer 79.0 vs 200 U/mL, P = .0006), associated with significantly lower frequencies of peripheral blood IgM memory B cells. To elucidate whether CML itself or treatment with TKI was responsible for the impaired humoral response, we assessed memory B-cell subsets in paired samples collected before and after imatinib therapy. Treatment with imatinib was associated with significant reductions in IgM memory B cells. In vitro coincubation of B cells with plasma from CML patients on TKI or with imatinib, dasatinib, or nilotinib induced significant and dose-dependent inhibition of Bruton's tyrosine kinase and indirectly its downstream substrate, phospholipase-C-γ2, both important in B-cell signaling and survival. These data indicate that TKIs, through off-target inhibition of kinases important in B-cell signaling, reduce memory B-cell frequencies and induce significant impairment of B-cell responses in CML.
Figures




References
-
- de Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS, et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: incidence of sustained responses in an intention-to-treat analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(20):3358–3363. - PubMed
-
- Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, et al. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(24):2260–2270. - PubMed
-
- Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, et al. ENESTnd Investigators. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(24):2251–2259. - PubMed
-
- Cwynarski K, Laylor R, Macchiarulo E, et al. Imatinib inhibits the activation and proliferation of normal T lymphocytes in vitro. Leukemia. 2004;18(8):1332–1339. - PubMed
-
- Mumprecht S, Matter M, Pavelic V, Ochsenbein AF. Imatinib mesylate selectively impairs expansion of memory cytotoxic T cells without affecting the control of primary viral infections. Blood. 2006;108(10):3406–3413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

