Distinct inspiratory rhythm and pattern generating mechanisms in the preBötzinger complex
- PMID: 23719793
- PMCID: PMC3737080
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4143-12.2013
Distinct inspiratory rhythm and pattern generating mechanisms in the preBötzinger complex
Abstract
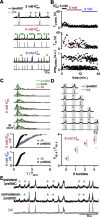
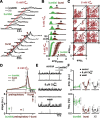
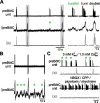
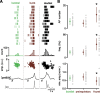
In the mammalian respiratory central pattern generator, the preBötzinger complex (preBötC) produces rhythmic bursts that drive inspiratory motor output. Cellular mechanisms initiated by each burst are hypothesized to be necessary to determine the timing of the subsequent burst, playing a critical role in rhythmogenesis. To explore mechanisms relating inspiratory burst generation to rhythmogenesis, we compared preBötC and hypoglossal (XII) nerve motor activity in medullary slices from neonatal mice in conditions where periods between successive inspiratory XII bursts were highly variable and distributed multimodally. This pattern resulted from rhythmic preBötC neural population activity that consisted of bursts, concurrent with XII bursts, intermingled with significantly smaller "burstlets". Burstlets occurred at regular intervals during significantly longer XII interburst intervals, at times when a XII burst was expected. When a preBötC burst occurred, its high amplitude inspiratory component (I-burst) was preceded by a preinspiratory component that closely resembled the rising phase of burstlets. Cadmium (8 μM) eliminated preBötC and XII bursts, but rhythmic preBötC burstlets persisted. Burstlets and preinspiratory activity were observed in ~90% of preBötC neurons that were active during I-bursts. When preBötC excitability was raised significantly, burstlets could leak through to motor output in medullary slices and in vivo in adult anesthetized rats. Thus, rhythmic bursting, a fundamental mode of nervous system activity and an essential element of breathing, can be deconstructed into a rhythmogenic process producing low amplitude burstlets and preinspiratory activity that determine timing, and a pattern-generating process producing suprathreshold I-bursts essential for motor output.
Figures


References
-
- Butera RJ, Jr, Rinzel J, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex: I. Bursting pacemaker neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999a;82:382–397. - PubMed
-
- Butera RJ, Jr, Rinzel J, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex: II. Populations of coupled pacemaker neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1999b;82:398–415. - PubMed
-
- Del Negro CA, Johnson SM, Butera RJ, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex: III. Experimental tests of model predictions. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:59–74. - PubMed
