Targeting breast cancer-initiating/stem cells with melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7/interleukin-24
- PMID: 23720015
- PMCID: PMC4334374
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.28289
Targeting breast cancer-initiating/stem cells with melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7/interleukin-24
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jul 1;139(1):E3. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30058. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27080528 No abstract available.
Abstract
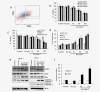
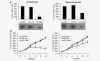
Melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7/interleukin-24 (mda-7/IL-24) displays a broad range of antitumor properties including cancer-specific induction of apoptosis, inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and modulation of antitumor immune responses. In our study, we elucidated the role of MDA-7/IL-24 in inhibiting growth of breast cancer-initiating/stem cells. Ad.mda-7 infection decreased proliferation of breast cancer-initiating/stem cells without affecting normal breast stem cells. Ad.mda-7 induced apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in breast cancer-initiating/stem cells similar to unsorted breast cancer cells and inhibited the self-renewal property of breast cancer-initiating/stem cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Prevention of inhibition of Wnt signaling by LiCl increased cell survival upon Ad.mda-7 treatment, suggesting that Wnt signaling inhibition might play a key role in MDA-7/IL-24-mediated death of breast cancer-initiating/stem cells. In a nude mouse subcutaneous xenograft model, Ad.mda-7 injection profoundly inhibited growth of tumors generated from breast cancer-initiating/stem cells and also exerted a potent "bystander" activity inhibiting growth of distant uninjected tumors. Further studies revealed that tumor growth inhibition by Ad.mda-7 was associated with a decrease in proliferation and angiogenesis, two intrinsic features of MDA-7/IL-24, and a reduction in vivo in the percentage of breast cancer-initiating/stem cells. Our findings demonstrate that MDA-7/IL-24 is not only nontoxic to normal cells and normal stem cells but also can kill both unsorted cancer cells and enriched populations of cancer-initiating/stem cells, providing further documentation that MDA-7/IL-24 might be a safe and effective way to eradicate cancers and also potentially establish disease-free survival.
Keywords: MDA-7/IL-24; Wnt signaling; apoptosis; breast cancer; cancer-initiating/stem cells.
Copyright © 2013 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: Nothing to report
Figures




References
-
- Goldhirsch A, Colleoni M, Domenighetti G, et al. Systemic treatments for women with breast cancer: outcome with relation to screening for the disease. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:1212–14. - PubMed
-
- Han JS, Crowe DL. Tumor initiating cancer stem cells from human breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2009;34:1449–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

