Immune and inflammatory role in renal disease
- PMID: 23720336
- PMCID: PMC3803162
- DOI: 10.1002/cphy.c120028
Immune and inflammatory role in renal disease
Abstract
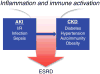
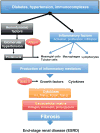
Chronic and acute renal diseases, irrespective of the initiating cause, have inflammation and immune system activation as a common underlying mechanism. The purpose of this review is to provide a broad overview of immune cells and inflammatory proteins that contribute to the pathogenesis of renal disease, and to discuss some of the physiological changes that occur in the kidney as a result of immune system activation. An overview of common forms of acute and chronic renal disease is provided, followed by a discussion of common therapies that have anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive effects in the treatment of renal disease.
Figures



References
-
- Abbate M, Zoja C, Corna D, Capitanio M, Bertani T, Remuzzi G. In progressive nephropathies, overload of tubular cells with filtered proteins translates glomerular permeability dysfunction into cellular signals of interstitial inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:1213–1224. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R. Anti-inflammatory effects of short-term pioglitazone therapy in men with advanced diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290:F600–F605. - PubMed
-
- Araki S, Haneda M, Koya D, Sugimoto T, Isshiki K, Chin-kanasaki M, Uzu T, Kashiwagi A. Predictive impact of elevated serum level of IL-18 for early renal dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: An observational follow-up study. Diabetologia. 2007;50:867–873. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson C, Qiao F, Song H, Gilkeson GS, Tomlinson S. Low-dose targeted complement inhibition protects against renal disease and other manifestations of autoimmune disease in MRL/lpr mice. J Immunol. 2008;180:1231–1238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

