Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a recombinant LigA fragment comprising repeat domains 4 to 7.5 as an antigen for diagnosis of equine leptospirosis
- PMID: 23720368
- PMCID: PMC3754523
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00245-13
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a recombinant LigA fragment comprising repeat domains 4 to 7.5 as an antigen for diagnosis of equine leptospirosis
Abstract
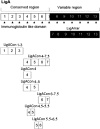
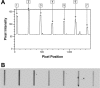
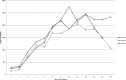
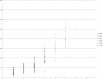
Leptospira immunoglobulin (Ig)-like (Lig) proteins are a novel family of surface-associated proteins in which the N-terminal 630 amino acids are conserved. In this study, we truncated the LigA conserved region into 7 fragments comprising the 1st to 3rd (LigACon1-3), 4th to 7.5th (LigACon4-7.5), 4th (LigACon4), 4.5th to 5.5th (LigACon4.5-5.5), 5.5th to 6.5th (LigACon5.5-6.5), 4th to 5th (LigACon4-5), and 6th to 7.5th (LigACon6-7.5) repeat domains. All 7 recombinant Lig proteins were screened using a slot-shaped dot blot assay for the diagnosis of equine leptospirosis. Our results showed that LigACon4-7.5 is the best candidate diagnostic antigen in a slot-shaped dot blot assay. LigACon4-7.5 was further evaluated as an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antigen for the detection of Leptospira antibodies in equine sera. This assay was evaluated with equine sera (n = 60) that were microscopic agglutination test (MAT) negative and sera (n = 220) that were MAT positive to the 5 serovars that most commonly cause equine leptospirosis. The indirect ELISA results showed that at a single serum dilution of 1:250, the sensitivity and specificity of ELISA were 80.0% and 87.2%, respectively, compared to those of MAT. In conclusion, an indirect ELISA was developed utilizing a recombinant LigA fragment comprising the 4th to 7.5th repeat domain (LigACon4-7.5) as a diagnostic antigen for equine leptospirosis. This ELISA was found to be sensitive and specific, and it yielded results that concurred with those of the standard MAT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serodiagnosis of equine leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using four recombinant protein markers.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014 Apr;21(4):478-83. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00649-13. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24451330 Free PMC article.
-
Serological analysis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant antigen LipL32 for the diagnosis of swine leptospirosis.Curr Microbiol. 2013 Feb;66(2):106-9. doi: 10.1007/s00284-012-0237-x. Epub 2012 Oct 14. Curr Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23064970
-
Recombinant ligA for leptospirosis diagnosis and ligA among the Leptospira spp. clinical isolates.J Microbiol Methods. 2008 Jan;72(1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2007.10.012. Epub 2007 Nov 17. J Microbiol Methods. 2008. PMID: 18079011
-
Diagnosis of human leptospirosis: systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of the Leptospira microscopic agglutination test, PCR targeting Lfb1, and IgM ELISA to Leptospira fainei serovar Hurstbridge.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Feb 7;24(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08935-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38326762 Free PMC article.
-
Equine genital leptospirosis: Evidence of an important silent chronic reproductive syndrome.Theriogenology. 2022 Oct 15;192:81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.08.029. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Theriogenology. 2022. PMID: 36063673 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant antigens rLipL21, rLoa22, rLipL32 and rLigACon4-8 for serological diagnosis of leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in dogs.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 19;9(12):e111367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111367. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25526513 Free PMC article.
-
Serodiagnosis of equine leptospirosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using four recombinant protein markers.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014 Apr;21(4):478-83. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00649-13. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24451330 Free PMC article.
-
Leptospiral Immunoglobulin-Like Domain Proteins: Roles in Virulence and Immunity.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 8;11:579907. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.579907. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33488581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moving towards the immunodiagnosis of staphylococcal intramammary infections.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Dec;33(12):2095-104. doi: 10.1007/s10096-014-2181-0. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24947175 Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of recombinant LigB protein and heat-killed antigen-based latex agglutination test with microscopic agglutination test for diagnosis of bovine leptospirosis.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2015 Oct;47(7):1329-35. doi: 10.1007/s11250-015-0867-7. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2015. PMID: 26065562
References
-
- Palaniappan RU, Ramanujam S, Chang YF. 2007. Leptospirosis: pathogenesis, immunity, and diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 20:284–292 - PubMed
-
- Divers TJ, Byars TD, Shin SJ. 1992. Renal dysfunction associated with infection of Leptospira interrogans in a horse. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 201:1391–1392 - PubMed
-
- Faisal SM, McDonough SP, Chang YF. 2012. Leptospira: invasion, pathogenesis and persistence, p 143–172 In Embers ME. (ed), The pathogenic spirochetes: strategies for evasion of host immunity and persistence. Springer Science, New York, NY
-
- Broux B, Torfs S, Wegge B, Deprez P, van Loon G. 2012. Acute respiratory failure caused by Leptospira spp. in 5 foals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 26:684–687 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

