Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a recombinant LigA fragment comprising repeat domains 4 to 7.5 as an antigen for diagnosis of equine leptospirosis
- PMID: 23720368
- PMCID: PMC3754523
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00245-13
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a recombinant LigA fragment comprising repeat domains 4 to 7.5 as an antigen for diagnosis of equine leptospirosis
Abstract
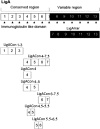
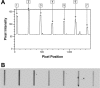
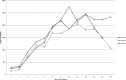
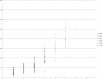
Leptospira immunoglobulin (Ig)-like (Lig) proteins are a novel family of surface-associated proteins in which the N-terminal 630 amino acids are conserved. In this study, we truncated the LigA conserved region into 7 fragments comprising the 1st to 3rd (LigACon1-3), 4th to 7.5th (LigACon4-7.5), 4th (LigACon4), 4.5th to 5.5th (LigACon4.5-5.5), 5.5th to 6.5th (LigACon5.5-6.5), 4th to 5th (LigACon4-5), and 6th to 7.5th (LigACon6-7.5) repeat domains. All 7 recombinant Lig proteins were screened using a slot-shaped dot blot assay for the diagnosis of equine leptospirosis. Our results showed that LigACon4-7.5 is the best candidate diagnostic antigen in a slot-shaped dot blot assay. LigACon4-7.5 was further evaluated as an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antigen for the detection of Leptospira antibodies in equine sera. This assay was evaluated with equine sera (n = 60) that were microscopic agglutination test (MAT) negative and sera (n = 220) that were MAT positive to the 5 serovars that most commonly cause equine leptospirosis. The indirect ELISA results showed that at a single serum dilution of 1:250, the sensitivity and specificity of ELISA were 80.0% and 87.2%, respectively, compared to those of MAT. In conclusion, an indirect ELISA was developed utilizing a recombinant LigA fragment comprising the 4th to 7.5th repeat domain (LigACon4-7.5) as a diagnostic antigen for equine leptospirosis. This ELISA was found to be sensitive and specific, and it yielded results that concurred with those of the standard MAT.
Figures

References
-
- Palaniappan RU, Ramanujam S, Chang YF. 2007. Leptospirosis: pathogenesis, immunity, and diagnosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 20:284–292 - PubMed
-
- Divers TJ, Byars TD, Shin SJ. 1992. Renal dysfunction associated with infection of Leptospira interrogans in a horse. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 201:1391–1392 - PubMed
-
- Faisal SM, McDonough SP, Chang YF. 2012. Leptospira: invasion, pathogenesis and persistence, p 143–172 In Embers ME. (ed), The pathogenic spirochetes: strategies for evasion of host immunity and persistence. Springer Science, New York, NY
-
- Broux B, Torfs S, Wegge B, Deprez P, van Loon G. 2012. Acute respiratory failure caused by Leptospira spp. in 5 foals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 26:684–687 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

