Characterization of a trifunctional glucosyltransferase essential for Moraxella catarrhalis lipooligosaccharide assembly
- PMID: 23720461
- PMCID: PMC3695755
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwt042
Characterization of a trifunctional glucosyltransferase essential for Moraxella catarrhalis lipooligosaccharide assembly
Abstract
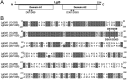
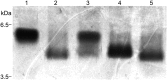
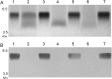
The human respiratory tract pathogen Moraxella catarrhalis expresses lipooligosaccharides (LOS), glycolipid surface moieties that are associated with enhanced colonization and virulence. Recent studies have delineated the major steps required for the biosynthesis and assembly of the M. catarrhalis LOS molecule. We previously demonstrated that the glucosyltransferase enzyme Lgt3 is responsible for the addition of at least one glucose (Glc) molecule, at the β-(1-4) position, to the inner core of the LOS molecule. Our data further suggested a potential multifunctional role for Lgt3 in LOS biosynthesis. The studies reported here demonstrate that the Lgt3 enzyme possesses two glycosyltransferase domains (A1 and A2) similar to that of other bifunctional glycosyltransferase enzymes involved in surface polysaccharide biosynthesis in Escherichia coli, Pasteurella multocida and Streptococcus pyogenes. Each Lgt3 domain contains a conserved DXD motif, shown to be involved in the catalytic activity of other glycosyltransferases. To determine the function of each domain, A1 (N-terminal), A2 (C-terminal) and double A1A2 site-directed DAD to AAA mutants were constructed and the resulting LOS phenotypes of these modified strains were analyzed. Our studies indicate that the Lgt3 N-terminal A1 catalytic domain is responsible for the addition of the first β-(1-3) Glc to the first Glc on the inner core. The C-terminal catalytic domain A2 then adds the β-(1-4) Glc and the β-(1-6) Glc, confirming the bifunctional nature of this domain. The results from these experiments demonstrate that Lgt3 is a novel, multifunctional transferase responsible for the addition of three Glcs with differing linkages onto the inner core of M. catarrhalis LOS.
Keywords: Moraxella catarrhalis; glucosyltransferase; lipooligosaccharide; trifunctional.
Figures

References
-
- Blixt O, van Die I, Norberg T, van den Eijnden DH. High-level expression of the Neisseria meningitidis lgtA gene in Escherichia coli and characterization of the encoded N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase as a useful catalyst in the synthesis of GlcNAc beta 1–>3Gal and GalNAc beta 1–>3Gal linkages. Glycobiology. 1999;9:1061–1071. doi:10.1093/glycob/9.10.1061. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ciucanu I, Kerek F. A simple and rapid method for the permethylation of carbohydrates. Carbohydr Res. 1984;131:209–217. doi:10.1016/0008-6215(84)85242-8. - DOI
-
- Coutinho PM, Deleury E, Davies GJ, Henrissat B. An evolving hierarchical family classification for glycosyltransferases. J Mol Biol. 2003;328:307–317. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00307-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cox AD, St Michael F, Cairns CM, Lacelle S, Filion AL, Neelamegan D, Wenzel CQ, Horan H, Richards JC. Investigating the potential of conserved inner core oligosaccharide regions of Moraxella catarrhalis lipopolysaccharide as vaccine antigens: Accessibility and functional activity of monoclonal antibodies and glycoconjugate derived sera. Glycoconj J. 2011;28:165–182. doi:10.1007/s10719-011-9332-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

