Coronary microvascular pericytes are the cellular target of sunitinib malate-induced cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 23720580
- PMCID: PMC3833098
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005066
Coronary microvascular pericytes are the cellular target of sunitinib malate-induced cardiotoxicity
Abstract
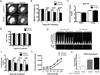
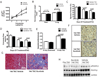
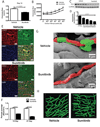
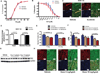
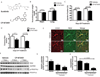
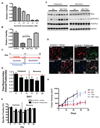
Sunitinib malate is a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of human malignancies. A substantial number of sunitinib-treated patients develop cardiac dysfunction, but the mechanism of sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity is poorly understood. We show that mice treated with sunitinib develop cardiac and coronary microvascular dysfunction and exhibit an impaired cardiac response to stress. The physiological changes caused by treatment with sunitinib are accompanied by a substantial depletion of coronary microvascular pericytes. Pericytes are a cell type that is dependent on intact platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) signaling but whose role in the heart is poorly defined. Sunitinib-induced pericyte depletion and coronary microvascular dysfunction are recapitulated by CP-673451, a structurally distinct PDGFR inhibitor, confirming the role of PDGFR in pericyte survival. Thalidomide, an anticancer agent that is known to exert beneficial effects on pericyte survival and function, prevents sunitinib-induced pericyte cell death in vitro and prevents sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity in vivo in a mouse model. Our findings suggest that pericytes are the primary cellular target of sunitinib-induced cardiotoxicity and reveal the pericyte as a cell type of concern in the regulation of coronary microvascular function. Furthermore, our data provide preliminary evidence that thalidomide may prevent cardiotoxicity in sunitinib-treated cancer patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cardio-oncology: it takes two to translate.Sci Transl Med. 2013 May 29;5(187):187fs20. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006490. Sci Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23720578 No abstract available.
References
-
- Di Lorenzo G, Autorino R, Bruni G, Carteni G, Ricevuto E, Tudini M, Ficorella C, Romano C, Aieta M, Giordano A, Giuliano M, Gonnella A, De Nunzio C, Rizzo M, Montesarchio V, Ewer M, De Placido S. Cardiovascular toxicity following sunitinib therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a multicenter analysis. Annals of Oncology. 2009 Sep;20:1535. - PubMed
-
- Schmidinger M, Zielinski CC, Vogl UM, Bojic A, Bojic M, Schukro C, Ruhsam M, Hejna M, Schmidinger H. Cardiac toxicity of sunitinib and sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2008 Nov 10;26:5204. - PubMed
-
- Khakoo AY, Kassiotis CM, Tannir N, Plana JC, Halushka M, Bickford C, 2nd, Trent J, Champion JC, Durand JB, Lenihan DJ. Heart failure associated with sunitinib malate: a multitargeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Cancer. 2008 Jun;112:2500. - PubMed
-
- Chu TF, Rupnick MA, Kerkela R, Dallabrida SM, Zurakowski D, Nguyen L, Woulfe K, Pravda E, Cassiola F, Desai J, George S, Morgan JA, Harris DM, Ismail NS, Chen JH, Schoen FJ, Van den Abbeele AD, Demetri GD, Force T, Chen MH. Cardiotoxicity associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Lancet. 2007 Dec 15;370:2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Richards CJ, Je Y, Schutz FA, Heng DY, Dallabrida SM, Moslehi JJ, Choueiri TK. Incidence and risk of congestive heart failure in patients with renal and nonrenal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2011 Sep 1;29:3450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

