Malignant pleural mesothelioma: incidence, etiology, diagnosis, treatment, and occupational health
- PMID: 23720698
- PMCID: PMC3659962
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0319
Malignant pleural mesothelioma: incidence, etiology, diagnosis, treatment, and occupational health
Abstract
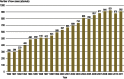
Background: The incidence of malignant mesothelioma in Germany is about 20 cases per million persons per year. Its association with asbestos exposure, usually occupational, has been unequivocally demonstrated. Even though the industrial use of asbestos was forbidden many years ago, new cases of mesothelioma continue to appear because of the long latency of the disease (median, 50 years). Its diagnosis and treatment still present a major challenge for ambulatory and in-hospital care and will do so for years to come.
Methods: This article is based on a selective review of the literature, along with data from the German Mesothelioma Register.
Results: 1397 people died of mesothelioma in Germany in 2010. A plateau in the incidence of the disease is predicted between 2015 and 2030. Most mesotheliomas arise from the pleura. The histological subtype and the Karnofsky score are the main prognostic factors. Only limited data are now available to guide treatment with a combination of the available methods (chemotherapy, surgery, radiotherapy). The prognosis is still poor, with a median survival time of only 12 months. Symptom control and the preservation of the patient's quality of life are the main aspects of care for patients with mesothelioma.
Conclusion: The incidence of mesothelioma is not expected to drop in the next few years. The available treatments are chemotherapy, surgery, and radiotherapy. Specialized treatment centers now increasingly provide multimodal therapy for treatment of mesothelioma.
Figures
Comment in
-
Progress means change: reflections on two articles about pleural disease.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 May;110(18):311-2. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0311. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 23720696 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Surgical therapeutic options.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Sep;110(39):660. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0660a. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24163708 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In reply.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013 Sep;110(39):660. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2013.0660b. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2013. PMID: 24163709 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Woitowitz H, Hillerdal G, Galvarezos A, Berghäuser K, Rödelsperger K, Jöckel K. Risiko und Einflussfaktoren des diffusen malignen Mesothelioms (DMM) Forschungsberichtsreihe FB 698. Bundesanstalt für Arbeitsschutz. 1993
-
- Scherpereel A, Astoul P, Baas P, et al. Guidelines of the European Respiratory Society and the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons for the management of malignant pleura mesothelioma. Eur Repir J. 2010;35:479–495. - PubMed
-
- Selikoff I, Churg J, Hammond E. Relation between exposure to asbestos and mesothelioma. N Eng J Med. 1965;272:560–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical