Emergence of 16S rRNA methylase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in hospitals in Vietnam
- PMID: 23721359
- PMCID: PMC3680199
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-251
Emergence of 16S rRNA methylase-producing Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates in hospitals in Vietnam
Abstract
Background: 16S rRNA methylase-producing Gram-negative bacteria are highly resistant to all clinically important aminoglycosides. We analyzed clinical strains of 16S rRNA methylase-producing Acinetobactor baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa obtained from clinical isolates in medical settings in Vietnam.
Methods: From 2008 to 2011, 101 clinical strains of A. baumannii and 15 of P. aeruginosa were isolated from patients in intensive care units (ICUs) in two medical settings in Vietnam. Antimicrobial susceptibilities were determined using the microdilution method and epidemiological analysis was performed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and MLST. Genes encoding the 16S rRNA methylases, OXAs and CTX-Ms were analyzed by PCR and sequence analysis.
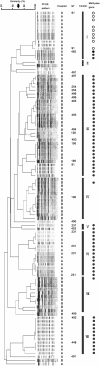
Results: 16S rRNA methylase-producing Gram-negative pathogens were detected in two hospitals in Vietnam. Of the 101 clinical isolates of A. baumannii and the 15 of P. aeruginosa isolated from two ICUs in these hospitals, 72 (71.3%) were highly resistant to amikacin, arbekacin and gentamicin, with MICs greater than 1,024 mg/L. The 16S rRNA methylases ArmA and RmtB were produced by 61 and 9 isolates of A. baumannii, respectively, and RmtB was produced by 2 isolates of P. aeruginosa. Moreover, 52 of the A. baumannii isolates producing 16S rRNA methylases harbored both blaOXA-23-like and blaOXA-51-like genes. Most A. baumannii isolates producing 16S rRNA methylase obtained in hospital A in Hanoi were ST91 and ST231, whereas most from hospital B in Ho Chi Minh City were ST136, ST195, and ST254.
Conclusions: Gram-negative bacteria producing the 16S rRNA methylases ArmA and RmtB are emerging in medical settings in Vietnam. A. baumannii isolates in northern and southern regions of Vietnam may be of different lineages.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

