Effects of demographics on the antihypertensive efficacy of triple therapy with amlodipine, valsartan, and hydrochlorothiazide for moderate to severe hypertension
- PMID: 23721363
- PMCID: PMC4098842
- DOI: 10.1185/03007995.2013.803057
Effects of demographics on the antihypertensive efficacy of triple therapy with amlodipine, valsartan, and hydrochlorothiazide for moderate to severe hypertension
Abstract
Objective: To compare the antihypertensive efficacy and safety of once-daily triple therapy with amlodipine (Aml) 10 mg, valsartan (Val) 320 mg, and hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 25 mg versus dual-therapy combinations of these components in patients with moderate to severe hypertension.
Research design: Subgroup analysis of a multinational, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, active-controlled trial.
Methods: After antihypertensive washout and a placebo run-in of up to 4 weeks, 2271 patients were randomly allocated in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to receive Aml/Val/HCTZ triple therapy or dual therapy with Val/HCTZ, Aml/Val, or Aml/HCTZ for 8 weeks. Forced titration to the full dose was done over the first 2 weeks of treatment. Efficacy and safety parameters were determined by age group (<65 vs. ≥65 years), gender, race (White vs. Black), ethnicity (Hispanic/Latino vs. non-Hispanic/Latino), and body mass index (BMI, <30 vs. ≥30 kg/m²).
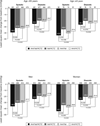
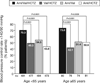
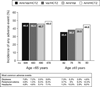
Main outcome measures: Change from baseline to endpoint in mean sitting systolic blood pressure (MSSBP) and mean sitting diastolic blood pressure (MSDBP); blood pressure (BP) control rate <140/90 mmHg.
Results: Triple therapy was numerically superior and, for the majority of comparisons, statistically superior to each dual therapy in reducing MSSBP and MSDBP and in improving BP control rates in all subgroups. Across subgroups, triple therapy reduced MSSBP by 5.7-10.7 mmHg more than Val/HCTZ, 3.4-8.3 mmHg more than Aml/Val, and 4.4-9.4 mmHg more than Aml/HCTZ. Triple therapy was well tolerated across all subgroups. Limitations of our analysis included the lack of stratification of patients by subgroup at randomization and the small sample size of some subgroups (e.g., Blacks, elderly).
Conclusions: Triple therapy with Aml/Val/HCTZ is effective and well tolerated in patients with moderate to severe hypertension regardless of age, gender, race, ethnicity, or BMI.
Trial registration number: NCT00327587.
Figures






References
-
- Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, et al. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49:69–75. - PubMed
-
- Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN. US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA. 2010;303:2043–2050. - PubMed
-
- Wolf-Maier K, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA. 2003;289:2363–2369. - PubMed
-
- August P. Initial treatment of hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:610–617. - PubMed
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003;42:1206–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
