Claudin 1 expression in basal-like breast cancer is related to patient age
- PMID: 23721519
- PMCID: PMC3674926
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-268
Claudin 1 expression in basal-like breast cancer is related to patient age
Abstract
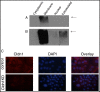
Background: Defects in tight junctions, gate-keepers of the integrity of the epidermal barrier function, are known to contribute to cancer development. As such, enhancing our understanding of how the expression of proteins involved in these junctions is regulated in cancer, remains a priority. Although the expression of one of these proteins, claudin 1, is down regulated in most invasive human breast cancers (HBC), we have recently shown that high levels of claudin 1, characterized tumors belonging to the very aggressive basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) subtype. In these tumors, the claudin 1 protein, usually localized in the cell membrane, is often mislocalized to the cytoplasm.
Methods: To examine the clinical relevance of this observation, we have generated and analyzed an invasive HBC tissue microarray consisting of 151 breast tumor samples; 79 of which presented a basal-like phenotype (i.e. ER-ve, PR-ve HER2-ve, CK5/6 or EGFR+ve). We also interrogated the outcome of claudin 1 knockdown in a human BLBC cell line, BT-20.
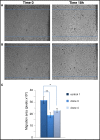
Results: Immunohistochemical analysis of this patient cohort revealed a significant association between high claudin 1 expression and BLBCs in women 55 years of age and older. Interestingly, no significant association was found between claudin 1 and nodal involvement, tumor grade or tumor size. Regression analysis however, showed a significant positive association between claudin 1 and claudin 4, even though claudin 4 did not significantly correlate with patient age. Claudin 1 knockdown in BT-20 cells resulted in decreased cell migration. It also significantly altered the expression of several genes involved in epithelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT); in particular, SERPINE 1 (PAI1) and SSP1 (osteopontin), known to inhibit EMT and cancer cell migration. Conversely, genes known to maintain EMT through their interaction, SNAIL2, TCF4 and FOXC2 were significantly down regulated.
Conclusions: The association of high claudin 1 protein levels observed in tumors derived from older women with BLBC, suggests that claudin 1 has the potential to serve as a marker which can identify a specific subgroup of patients within the BLBC subtype and thus, further contribute to the characterization of these ill-defined breast cancers. More importantly, our studies strongly suggest that claudin 1 directly participates in promoting breast cancer progression, possibly through the alteration of expression of EMT genes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Claudin expression in high-grade invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast: correlation with the molecular subtype.Mod Pathol. 2013 Apr;26(4):485-95. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.187. Epub 2012 Dec 7. Mod Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23222490 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins 1, 3, and 4 protein expression in ER negative breast cancer correlates with markers of the basal phenotype.Virchows Arch. 2009 Jun;454(6):647-56. doi: 10.1007/s00428-009-0770-6. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Virchows Arch. 2009. PMID: 19387682
-
Dietary energy balance modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor progression in murine claudin-low and basal-like mammary tumor models.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012 Jul;5(7):930-42. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-12-0034. Epub 2012 May 15. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012. PMID: 22588949 Free PMC article.
-
[Is there a claudin-low phenotype of breast cancer?].Arkh Patol. 2022;84(1):45-49. doi: 10.17116/patol20228401145. Arkh Patol. 2022. PMID: 35166478 Review. Russian.
-
Research progress of Claudin-low breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 11;13:1226118. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1226118. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37904877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Claudin 1 Transcript Variants in Human Invasive Breast Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 20;11(9):e0163387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163387. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27649506 Free PMC article.
-
Nectin4 is a potential therapeutic target for asthma.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 15;13:1049900. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1049900. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36457999 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Fixation Methods for the Detection of Claudin 1 and E-Cadherin in Breast Cancer Cell Lines by Immunofluorescence.J Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Feb;70(2):181-187. doi: 10.1369/00221554211055240. Epub 2021 Oct 29. J Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 34715746 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins as biomarkers of differential diagnosis and prognosis of tumors.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Oct;147(10):2803-2817. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03725-0. Epub 2021 Jul 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34241653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Claudins in cancer: bench to bedside.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Jan;469(1):55-67. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1877-7. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 27624415 Review.
References
-
- Nicholson RI, Johnston SR. Endocrine therapy–current benefits and limitations. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;93(Suppl 1):S3–S10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

