A genetic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in adult-onset Still's disease
- PMID: 23721694
- PMCID: PMC4060242
- DOI: 10.1186/ar4239
A genetic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in adult-onset Still's disease
Abstract
Introduction: Adult-onset still's disease (AOSD) is a rare systemic inflammatory disorder in which abnormalities in inflammatory cytokines production appear to play a pathophysiological role. Our previous work has reported increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and revealed its correlation with disease severity and activity in AOSD. A -173 G/C single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (rs755622) and a -794 CATT₅₋₈ repeat (rs5844572) in the MIF promoter have been reported. In this study, we sought to explore the relationship between functional MIF promoter polymorphisms and MIF expression in AOSD.
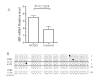
Methods: 100 patients and 200 controls were recruited in the study. A polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay was utilized to analyze the -173 G/C SNP (rs755622) and PCR-based size discrimination assay was applied to detect the -794 CATT₅₋₈ repeat (rs5844572) in the MIF promoter. Plasma MIF levels were measured by ELISA. MIF mRNA levels were quantified by real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. Bisulfate genomic sequencing was employed to evaluate DNA methylation status within the MIF promoter.
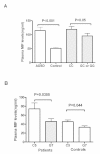
Results: We identified that the frequencies of MIF -794 CATT₅ (P = 0.001) allele and the expression of MIF (P <0.001) were increased in patients compared to healthy controls. Plasma levels of MIF in patients with CC genotype were higher than those of patients with GC or GG genotypes (P = 0.05). In patients with established AOSD, a higher frequency of -794 CATT₇ containing MIF genotypes was observed in those with liver dysfunction (P = 0.009). Haplotype analysis revealed a higher representation of the MIF haplotype defined by -173*C/-794 CATT₅ (C5) in AOSD patients (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Functional promoter polymorphisms in the MIF gene influence plasma MIF levels in AOSD and may contribute to disease susceptibility or clinical presentation of AOSD.
Figures
References
-
- Pouchot J, Sampalis JS, Beaudet F, Carette S, Décary F, Salusinsky-Sternbach M, Hill RO, Gutkowski A, Harth M, Myhal D. et al. Adult Still's disease: manifestations, disease course, and outcome in 62 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1991;15:118–136. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino T, Ohta A, Yang D, Kawamoto M, Kikuchi M, Inoue Y, Kamizono S, Ota T, Itoh K, Oizumi K. Elevated serum interleukin-6, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in patients with adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1998;15:396–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

