The Nrf2/SKN-1-dependent glutathione S-transferase π homologue GST-1 inhibits dopamine neuron degeneration in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of manganism
- PMID: 23721876
- PMCID: PMC3773487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2013.05.014
The Nrf2/SKN-1-dependent glutathione S-transferase π homologue GST-1 inhibits dopamine neuron degeneration in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of manganism
Abstract
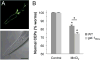
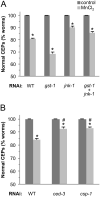
Exposure to high levels of manganese (Mn) results in a neurological condition termed manganism, which is characterized by oxidative stress, abnormal dopamine (DA) signaling, and cell death. Epidemiological evidence suggests correlations with occupational exposure to Mn and the development of the movement disorder Parkinson's disease (PD), yet the molecular determinants common between the diseases are ill-defined. Glutathione S-transferases (GSTs) of the class pi (GSTπ) are phase II detoxification enzymes that conjugate both endogenous and exogenous compounds to glutathione to reduce cellular oxidative stress, and their decreased expression has recently been implicated in PD progression. In this study we demonstrate that a Caenorhabditis elegans GSTπ homologue, GST-1, inhibits Mn-induced DA neuron degeneration. We show that GST-1 is expressed in DA neurons, Mn induces GST-1 gene and protein expression, and GST-1-mediated neuroprotection is dependent on the PD-associated transcription factor Nrf2/SKN-1, as a reduction in SKN-1 gene expression results in a decrease in GST-1 protein expression and an increase in DA neuronal death. Furthermore, decreases in gene expression of the SKN-1 inhibitor WDR-23 or the GSTπ-binding cell death activator JNK/JNK-1 result in an increase in resistance to the metal. Finally, we show that the Mn-induced DA neuron degeneration is independent of the dopamine transporter DAT, but is largely dependent on the caspases CED-3 and the novel caspase CSP-1. This study identifies a C. elegans Nrf2/SKN-1-dependent GSTπ homologue, cell death effectors of GSTπ-associated xenobiotic-induced pathology, and provides the first in vivo evidence that a phase II detoxification enzyme may modulate DA neuron vulnerability in manganism.
Keywords: Caspase; DA; ECL; GFP; Manganism; Neurodegeneration; Neurotoxicity; Nrf2; PAGE; PD; Parkinson's disease; ROS; SN; TH; WT; dopamine; enhanced chemiluminescence; green fluorescent protein; polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; reactive oxygen species; substantia nigra; tyrosine hydroxylase; wild type.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement: The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bradford M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

