Effect of temperature on the orthodontic clinical applications of NiTi closed-coil springs
- PMID: 23722142
- PMCID: PMC3731104
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.19073
Effect of temperature on the orthodontic clinical applications of NiTi closed-coil springs
Abstract
NiTi spring coils were used to obtain large deformation under a constant force. The device consists on a NiTi coil spring, superelastic at body temperature, in order to have a stress plateau during the austenitic retransformation during the unloading. The temperature variations induced changes in the spring force.
Objectives: The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of the temperature variations in the spring forces and corrosion behaviour simulating the ingestion hot/cold drinks and food.
Study design: The springs were subjected to a tensile force using universal testing machine MTS-Adamel (100 N load cell). All tests were performed in artificial saliva maintained at different temperatures. The corrosion tests were performed according to the ISO-standard 10993-15:2000.
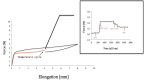
Results: The increase in temperature of 18 °C induced an increase in the spring force of 30%. However, when the temperature returns to 37 °C the distraction force recovers near the initial level. After cooling down the spring to 15 °C, the force decreased by 46%. This investigation show as the temperature increase, the corrosion potential shifts towards negative values and the corrosion density is rising.
Conclusions: The changes of the temperatures do not modify the superelastic behaviour of the NiTi closed-coil springs. The corrosion potential of NiTi in artificial saliva is decreasing by the rise of the temperatures.
Figures
References
-
- Idelsohn S, Pe-a J, Lacroix D, Planell JA, Gil FJ, Arcas A. Continuous mandibular distraction osteogenesis using superelastic shape memory alloy (SMA) J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15:541–6. - PubMed
-
- SuÃrez C, Vilar T, Gil J, Sevilla P. In vitro evaluation of surface topographic changes and nickel release of lingual orthodontic archwires. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21:675–83. - PubMed
-
- Espinar E, Llamas J. M, Michiardi A, Ginebra M.P, Gil F.J. Reduction of Ni release and improvement of the friction behavior of NiTi orthodontic archwires by oxidation treatments. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22:1119–25. - PubMed
-
- Brantley WA, Iijima M, Grentzer TH. Temperature modulated DSC provides new insight about nickel-titanium wire transformations. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 2003;124:387–94. - PubMed
-
- Sfondrini MF, Cacciafesta V, Maffia E, Scribante A, Alberti G, Biesuz R. Nickel release from new conventional stainless steel, recycled, and nickel-free orthodontic brackets: An in vitro study. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2010;137:809–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources